Does Epididymitis Cause Premature Ejaculation?

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Satadeepa is a Psychologist with 5 years of experience in the field of mental health and holds a Master's Degree in Clinical Psychology. Her areas of work interest and specialization include anxiety & mood disroders, relationship issues, self esteem development, grief, behavioural sleep medicine and sexual wellness.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 27 May, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.

"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
Have you ever wondered if there is a connection between epididymitis and premature ejaculation? In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the possible link between these two conditions and provide an in-depth analysis of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available.
What is Epididymitis?
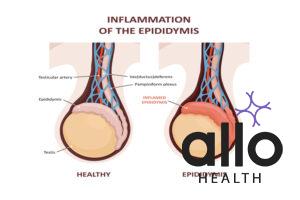
This is a medical condition that occurs when the epididymis, a coiled tube located at the back of the testicles, becomes inflamed due to bacterial or viral infection, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), or injury.
The condition can be diagnosed through physical examination, medical history, and tests such as urine sample, blood tests, and ultrasound. Treatment for epididymitis includes antibiotics, pain relievers, rest, and applying cold compresses to the affected area. It is essential to treat it promptly to prevent complications such as chronic epididymitis, infertility, and abscess formation.
Types of Epididymitis
Acute Epididymitis
This is the most common type of epididymitis and is typically caused by a bacterial infection. It often develops rapidly, with symptoms appearing within a few days. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles
- Tenderness in the affected area
- A lump or mass in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Pain during ejaculation
- Discharge from the penis
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
It can be caused by a variety of bacteria, including E. coli, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. It is most commonly seen in sexually active men, although it can also be caused by other factors such as urinary tract infections, prostatitis, and structural abnormalities.
Chronic Epididymitis
This type of epididymitis that lasts for at least three months. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial infections, structural abnormalities, and autoimmune disorders. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and discomfort in one or both testicles
- Tenderness in the affected area
- A lump or mass in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Pain during ejaculation
- Discharge from the penis
- Enlargement of the epididymis
- Groin pain
It often develops slowly over time. It can also be more difficult to diagnose and treat, as the underlying causes can be more complex.
Recurrent Epididymitis
This is a type of epididymitis that occurs repeatedly over time. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic bacterial infections, structural abnormalities, and immune system disorders. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and discomfort in one or both testicles
- Tenderness in the affected area
- A lump or mass in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Pain during ejaculation
- Discharge from the penis
- Enlargement of the epididymis
- Groin pain
It can be difficult to treat, as the underlying causes can be difficult to identify and address. However, it is important to seek medical attention for recurrent epididymitis, as this condition can lead to serious health complications over time.
Tuberculous Epididymitis
This is a rare type of epididymitis that is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can occur in men who have tuberculosis elsewhere in the body, such as in the lungs. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and discomfort in one or both testicles
- Tenderness in the affected area
- A lump or mass in the scrotum
- Enlargement of the epididymis
- Pus or fluid drainage from the affected area
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin
This type can be difficult to diagnose, as it can present with symptoms similar to other types of epididymitis. Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, imaging tests such as ultrasound, and tests to identify the presence of tuberculosis bacteria.
Traumatic Epididymitis
This is a type of epididymitis that occurs as a result of trauma or injury to the scrotum. This can include physical trauma such as a direct blow to the scrotum, or a sudden twisting or torsion of the testicles. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles
- Tenderness in the affected area
- A lump or mass in the scrotum
- Bruising or discoloration of the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Pain during ejaculation
Treatment typically involves rest and pain management, although surgery may be required in severe cases.
Idiopathic Epididymitis
This is a type of epididymitis that occurs without a known cause. It can be difficult to diagnose and treat, as the underlying causes are often unknown. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and discomfort in one or both testicles
- Tenderness in the affected area
- A lump or mass in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Pain during ejaculation
Treatment typically involves pain management and rest. In some cases, antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms.
What is Premature Ejaculation?

Premature ejaculation is a sexual dysfunction that occurs when a man ejaculates before he or his partner desires during sexual intercourse. It can be classified into two types: primary premature ejaculation, which occurs from the first sexual experience, and secondary premature ejaculation, which occurs after a period of normal sexual function.
The causes of premature ejaculation can be physical, psychological, or a combination of both. Physical causes include prostate concerns, thyroid concerns, hormonal imbalances, and neurological disorders. Psychological causes include anxiety, depression, stress, and relationship concerns.
The diagnosis of premature ejaculation is based on the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and the duration of sexual intercourse before ejaculation. Treatment for premature ejaculation includes behavioral techniques, medications, and counseling.
The Connection Between Epididymitis and Premature Ejaculation
There is no direct link between epididymitis and premature ejaculation in patients. Epididymitis does not cause premature ejaculation, nor does premature ejaculation cause epididymitis.
However, epididymitis and premature ejaculation can have indirect links due to their effects on sexual function. Epididymitis can cause pain and discomfort during sexual activity, which can lead to anxiety and stress. These psychological factors can affect sexual performance and cause premature ejaculation.
Similarly, premature ejaculation can cause anxiety and stress, leading to performance anxiety and erectile dysfunction. Erectile dysfunction can cause difficulty in achieving or maintaining an erection, which can result in pain during sexual activity and increase the risk of epididymitis.
Common Causes
- Bacterial infections: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea are common causes in sexually active men.
- Non-sexually transmitted infections: Infections such as urinary tract infections or prostatitis can also lead to the condition
- Trauma or injury: Physical injury to the groin area can result in inflammation of the epididymis.
- Other medical conditions: Autoimmune diseases, such as Behçet’s disease, can cause the condition in some cases.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms
- Pain and swelling in the affected testicle
- Redness and warmth in the scrotum
- Fever
- Discharge from the penis
- Pain during ejaculation or urination
Diagnosis
- Perform a physical examination
- Order tests to identify the cause of the infection, such as a urine test or a swab of the urethra
- Request imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, to visualize the epididymis and rule out other conditions
Common Treatment Suggestions for Epididymitis

Medical Treatment Options
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are a commonly prescribed treatment for bacterial epididymitis infection in patients. The specific antibiotic prescribed will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection. The most common antibiotics used to treat the condition include fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, and macrolides. The duration of antibiotic treatment may vary, but it typically lasts between 10 and 14 days.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medication: Non-bacterial epididymitis may be treated with anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen. These medications can help to reduce pain and swelling in the scrotum. In some cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to further reduce inflammation.
- Pain Management: Pain management techniques such as ice packs or warm compresses may also be used to alleviate discomfort caused by pididymitis. Resting and elevating the scrotum may also help to reduce pain and swelling. You can reduce the pain and swelling by consuming over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be required. This may be necessary if an abscess or blockage is present in the epididymis. Surgery may also be required if the infection has spread to other parts of the reproductive system.
Natural Remedies
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs may have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help to reduce inflammation and fight off infections. Some herbs that may be beneficial for the condition include saw palmetto, echinacea, and garlic. These herbs can be taken as supplements or added to teas or tinctures.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for digestive health. Some research suggests that probiotics may also help to prevent and treat infections in the urogenital tract, including epididymitis. Probiotic supplements can be taken orally, or probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt or kefir can be added to the diet.
- Essential Oils: Certain essential oils may have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help to reduce inflammation and fight off infections. Some essential oils that may be beneficial for epididymitis include tea tree oil, lavender oil, and eucalyptus oil. These oils can be diluted and applied topically to the scrotum, or added to a warm bath for a soothing effect.
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle changes such as maintaining good hygiene, regular exercise, avoiding tight clothing, and abstaining from sexual activity may also help to prevent and alleviate symptoms of the condition. Maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly can also help to support overall reproductive health.
Risk Factors of Epididymitis
- Sexual activity: Men who are sexually active are at a higher risk of developing the condition, particularly if they engage in unprotected sex. This is because sexual activity can introduce bacteria or viruses into the urethra, which can then travel to the epididymis and cause inflammation.
- Urinary tract infections: UTIs can cause inflammation and irritation in the urethra, which can then spread to the epididymis. Men who have a history of UTIs are at a higher risk of developing the condition.
- Prostatitis: Prostatitis is a condition that affects the prostate gland, which is located near the base of the bladder. Prostatitis can cause inflammation in the urethra, which can then spread to the epididymis. Men who have a history of prostatitis are at a higher risk of developing the condition
- Uncircumcised penis: Men who have an uncircumcised penis are at a higher risk of developing the condition This is because the foreskin can trap bacteria and other pathogens, which can then lead to infection and inflammation.
- Catheterization: Men who have undergone catheterization, a procedure in which a tube is inserted into the bladder to drain urine, are at a higher risk of developing the condition. This is because catheterization can introduce bacteria into the urethra, which can then travel to the epididymis and cause inflammation.
- Structural abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract can also increase the risk of developing the condition. These abnormalities can include urethral strictures, which are narrow areas in the urethra that can obstruct the flow of urine, or bladder diverticula, which are small pouches that can form in the bladder.
- Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression, which can occur as a result of certain medications or medical conditions, can increase the risk of developing the condition. This is because a weakened immune system can make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections.
- Age: The condition is most prevalent in men aged between 19 and 35 years old, although it can occur in males of all ages.
- Personal hygiene: Poor personal hygiene practices can also increase the risk of developing the condition. Men who do not practice good hygiene, such as failing to clean the genital area properly, are at a higher risk of developing infections that can lead to the condition
- Substance abuse: Substance abuse, including alcohol and drug abuse, can also increase the risk of developing the condition. This is because substance abuse can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections.
- Previous surgery: Men who have undergone previous surgery in the genital area, such as a vasectomy or hernia repair, are at a higher risk of developing the condition. This is because surgery can cause scarring and damage to the epididymis, making it more susceptible to infection and inflammation.
Final Words:
Although epididymitis and premature ejaculation are distinct conditions, there is a potential connection between the two. Inflammation of the epididymis can cause discomfort and anxiety, which may contribute to premature ejaculation. Treating epididymitis may help alleviate these concerns, improving sexual function and satisfaction.
If you suspect that you have epididymitis or are struggling with premature ejaculation, seek medical advice from a health care provider to discuss your symptoms and receive appropriate treatment.
Remember to practice safe sex, maintain proper hygiene, and seek prompt medical attention for any related conditions to help prevent epididymitis and its potential complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can epididymitis lead to infertility?
A: Although rare, untreated or chronic epididymitis can result in reduced fertility due to scarring and obstruction of the epididymis, which can impede sperm transport.
Q: Can epididymitis be prevented?
A: Practicing safe sex, maintaining proper hygiene, and seeking prompt medical expert advice for urinary tract infections or other related conditions can help reduce the risk of developing epididymitis.
Q: Does treating epididymitis improve premature ejaculation?
A: Treating epididymitis may alleviate discomfort and anxiety related to sexual activity, potentially leading to an improvement in premature ejaculation. However, the success of treatment of epididymitis depends on the individual and the severity of the condition, consult the doctor about treatment options.
Q: Are there any specific exercises or therapies to help with premature ejaculation?
A: Behavioral techniques, such as the “stop-start” method, can help with premature ejaculation. Pelvic floor exercises (Kegels) can also be beneficial. In some cases, professional counseling or sex therapy may be recommended.







































