Exploring The Relationship Between Diabetes and Sex

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Ms Rachel graduated with a MSc. in clinical psychology from CMR university, Bangalore. With close to two years of experience in the field of Child and Adolescent Psychology.

Anoush Gomes is a seasoned Content Writer with over 10 years of experience, specializing in various writing styles such as medical content, creative writing, storytelling, and research papers. Anoush embarked on a unique journey, starting with pre-medical studies at the Dante Aligheri Academy and the University of Miami, where she earned a Bachelor's degree with a major in Biology and a minor in Psychology. Having pursued medical school and completed clinicals, Anoush transitioned to the world of medical content writing, where her passion for both healthcare and writing converged. Her writing skills encompass persuasive, narrative, expository, and descriptive styles, making complex medical concepts accessible to diverse audiences. Beyond her professional endeavors, Anoush is a multi-faceted individual with a rich tapestry of interests. A writer, artist, poet, avid reader, certified nerd, and hopeful author, she finds inspiration in the intersection of creativity and science. Whether crafting engaging medical narratives or weaving captivating stories, Anoush combines her diverse background and writing expertise to deliver compelling content that resonates with diverse audiences.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 22 May, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.

"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease that affects the way the body produces or uses insulin. A hormone called insulin controls the body’s blood sugar levels. Diabetes develops when the body’s blood sugar levels rise due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective insulin usage. Diabetes can lead to a host of complications, one of which is sexual dysfunction.
Physical, psychological, and hormonal imbalances are just a few of the causes of sexual dysfunction. Let’s explore the biology of diabetes that affects sexual health, the symptoms of diabetes that affect sexual health, the sexual dysfunctions caused by diabetes, and the medications given to those with sexual health conditions and diabetes.
What is Diabetes?
High blood sugar levels result from diabetes, a metabolic condition in which the body is unable to adequately make or use insulin. The pancreas secretes the hormone insulin, which controls blood glucose levels. When insulin is not produced or used effectively, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to hyperglycemia.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes: This is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in childhood or adolescence and requires insulin injections for life.
Type 2 diabetes: This is the most common type of diabetes and is usually caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet. Type 2 diabetes can usually be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, or insulin injections.
Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after delivery. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Biology of Diabetes That Affects Sexual Health
Diabetes can cause several physiological changes in the body that can lead to sexual dysfunction. One of the main physiological changes caused by diabetes is nerve damage or neuropathy. High blood sugar levels can cause damage to the nerves that control the blood vessels and muscles in the genital area. This damage can affect the ability to achieve and maintain an erection in men and to achieve sexual arousal and orgasm in women. Neuropathy can also lead to decreased sensation in the genital area, making it difficult to achieve sexual pleasure.
Diabetes can also cause vascular damage, which can affect sexual health. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels that supply blood to the penis and clitoris. This damage can lead to reduced blood flow to these areas, making it difficult to achieve and maintain an erection or sexual arousal. Vascular damage can also lead to decreased lubrication in women, making sexual intercourse painful or uncomfortable.
Symptoms of Diabetes That Affect Sexual Health
There are several symptoms of diabetes that can affect sexual health. One of the most common symptoms is fatigue. Fatigue can make it difficult to have the energy and desire for sexual activity. High blood sugar levels can also cause frequent urination, which can interfere with sexual activity. Frequent urination can disrupt sexual activity and lead to embarrassment or discomfort.
Another symptom of diabetes that can affect sexual health is erectile dysfunction in men. Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection that is firm enough for sexual intercourse. Men with diabetes are more likely to experience erectile dysfunction than men without diabetes. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels that control the penis, making it difficult to achieve and maintain an erection.
Women with diabetes may experience decreased sexual desire, difficulty achieving sexual arousal, and difficulty achieving orgasm. These symptoms may be related to nerve damage, vascular damage, or hormonal imbalances caused by diabetes.
Sexual Dysfunctions Caused by Diabetes

Diabetes can cause sexual dysfunction in several ways. Here are some of the ways in which diabetes can cause sexual dysfunction:
Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can lead to the damage of the nerves that contrsexual function, leading to sexual dysfunction.
Vascular damage: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels that supply blood to the sexual organs, leading to reduced blood flow and sexual dysfunction.
Hormonal imbalances: Diabetes can cause imbalances in the hormones that regulate sexual function, leading to sexual dysfunction.
Psychological factors: Diabetes can cause psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and stress, which can contribute to sexual dysfunction.
Types of Sexual Dysfunction in Men with Diabetes
Erectile dysfunction (ED): ED is the most common sexual dysfunction in men with diabetes. Diabetes can damage the nerves and blood vessels that control erections, leading to difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
Diabetes can cause erectile dysfunction (ED) in several ways:
Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control blood flow to the penis. This can lead to decreased sensitivity and difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
Blood vessel damage: Diabetes can damage blood vessels throughout the body, including those that supply blood to the penis. This can result in reduced blood flow to the penis and make it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
Hormonal changes: Diabetes can affect the production of hormones that play a role in sexual function, such as testosterone.
Psychological factors: Diabetes can cause psychological stress, anxiety, and depression, which can all contribute to erectile dysfunction.
Retrograde ejaculation: Retrograde ejaculation is a condition in which semen is enters the bladder instead of out of the penis during orgasm. This is caused by nerve damage and can result in infertility.
Diabetes can cause retrograde ejaculation by affecting the nerves that control the bladder and the muscles that surround the bladder and urethra. Normally during ejaculation, the muscles at the neck of the bladder tighten, preventing semen from entering the bladder and instead propelling it out through the urethra.
However, in people with diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control these muscles, leading to dysfunction of the muscle contractions. This can result in the muscles not functioning properly during ejaculation, causing the semen to flow backward into the bladder instead of being expelled out through the penis.
This condition is called retrograde ejaculation, and it can cause infertility in men. Treatment for retrograde ejaculation in men with diabetes may include medications to help the bladder neck muscles close tightly during ejaculation or adjusting diabetes management to improve blood sugar control.
Peyronie’s disease: Peyronie’s disease is a condition in which scar tissue forms inside the penis, causing it to bend or curve abnormally during an erection. Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
One possible connection between diabetes and Peyronie’s disease is that both conditions can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves. In people with diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body, including those that supply the penis. This damage can impair blood flow to the penis and affect the ability to get and maintain an erection. Similarly, Peyronie’s disease can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves in the penis, which can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
Additionally, some studies have suggested that there may be a link between Peyronie’s disease and insulin resistance, a hallmark feature of type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance occurs when the body becomes less responsive to the hormone insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. Some researchers believe that insulin resistance may contribute to the development of Peyronie’s disease by promoting inflammation and scar tissue formation in the penis.
Premature ejaculation: Premature ejaculation is more common in men with diabetes, likely due to nerve damage. Diabetes can cause premature ejaculation (PE) through several mechanisms, including:
Nerve damage (neuropathy): High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control sexual response, including those in the genitals. This can lead to a loss of control over the ejaculation reflex, resulting in premature ejaculation.
Erectile dysfunction (ED): Diabetes can cause ED, which can in turn lead to premature ejaculation. When a man has difficulty getting or maintaining an erection, he may ejaculate prematurely due to the heightened sensitivity of the penis during sexual activity.
Psychological factors: The stress of living with diabetes can also impact a person’s mental health and sexual function. Diabetes can cause anxiety, depression, and other emotional concerns that can lead to PE.
Hormonal imbalances: Diabetes can affect the balance of hormones in the body, including testosterone and estrogen, which play a role in sexual function. If these hormones are imbalanced, it can lead to concerns with ejaculation.
Types of Sexual Dysfunction in Women with Diabetes
Vaginal dryness: Diabetes can cause reduced blood flow and nerve damage to the vagina, leading to a lack of lubrication and discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse. Diabetes can cause vaginal dryness in several ways:
- Decreased blood flow: Diabetes can damage blood vessels, which can lead to decreased blood flow to the vaginal area. This can cause a decrease in lubrication and result in vaginal dryness.
Nerve damage: Diabetes can also damage nerves that control sexual function and vaginal lubrication. This can lead to a decrease in natural lubrication and make sexual activity uncomfortable or painful.
Hormonal imbalances: Diabetes can also cause hormonal imbalances, such as a decrease in estrogen levels. This can lead to vaginal dryness and other symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and mood changes.
Increased risk of infections: High blood sugar levels can also increase the risk of vaginal infections, which can cause inflammation and irritation in the vaginal area, leading to dryness.
Reduced libido: Hormonal imbalances caused by diabetes can lead to a decreased sex drive in women. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to fatigue which can lead to reduced libido.
Orgasmic dysfunction: Diabetes can cause nerve damage and reduced blood flow to the clitoris, making it difficult to achieve orgasm.
Dyspareunia: Dyspareunia is a condition in which sexual intercourse is painful. Diabetes can cause nerve damage and reduced blood flow to the vagina, leading to dyspareunia.
One of the ways diabetes can cause orgasmic dysfunction is by damaging the nerves that control sexual function. Diabetes can cause peripheral neuropathy, which is nerve damage that affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, including those that control sexual function. This nerve damage can interfere with the normal sexual response cycle, leading to difficulty achieving or delaying orgasm.
In addition to nerve damage, diabetes can also cause vascular concerns, such as atherosclerosis, which is a hardening and narrowing of the arteries. This can affect blood flow to the genitals and impair sexual function.
Other factors that may contribute to orgasmic dysfunction in people with diabetes include medications used to manage diabetes, hormonal imbalances, and psychological factors such as anxiety or depression.
Managing Diabetes And Sexual Health
Managing diabetes effectively is essential to maintaining good sexual health. The following are some tips on how to manage diabetes and sexual health.
Control Blood Sugar Levels
The most important aspect of managing diabetes is controlling blood sugar levels. Keeping blood sugar levels within a healthy range can reduce the risk of complications, including those that affect sexual health. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing blood sugar levels, which may include medication, diet, and exercise.
Communicate With Your Healthcare Provider
It is essential to communicate with your healthcare provider about any sexual health concerns you may have. Your healthcare provider can provide advice and treatment options to help manage any sexual health concerns you may experience.
Practice Safe Sex
Practicing safe sex is essential for reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections. Use condoms to protect against sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancy.
Use Lubrication
If you experience vaginal dryness, using lubrication can make sex more comfortable. Choose a water-based lubricant that is safe for use with condoms.
Try Erectile Dysfunction Medication
If you experience erectile dysfunction, your healthcare provider may prescribe medication to help manage the condition. Medications like sildenafil and tadalafil can help improve blood flow to the penis, making it easier to achieve and maintain an erection.
Seek Help for Premature Ejaculation
If you experience premature ejaculation, there are various treatment options available. These include behavioral techniques, medications, and counseling.
Manage Stress
Stress can impact sexual health, so managing stress is essential for maintaining good sexual health. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Medications Given to Those With Sexual Health Conditions And Diabetes
There are several medications available to treat sexual health conditions in people with diabetes. For men with erectile dysfunction, there are several medications available to treat erectile dysfunction. One of the most commonly prescribed medications is sildenafil, which is sold under the brand name Viagra. Sildenafil works by increasing blood flow to the penis, making it easier to achieve and maintain an erection. Other medications that can be used to treat erectile dysfunction include tadalafil and vardenafil.
For women with sexual dysfunction caused by diabetes, there are several treatment options available. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can be used to replace estrogen and progesterone in women who are experiencing hormonal imbalances. HRT can help to alleviate symptoms such as vaginal dryness, decreased libido, and difficulty achieving orgasm.
Another treatment option for women with sexual dysfunction caused by diabetes is the use of vaginal lubricants. Vaginal lubricants can be used to increase lubrication and reduce discomfort during sexual activity. There are several different types of vaginal lubricants available, including water-based, oil-based, and silicone-based lubricants.
Counseling and therapy can also be effective treatments for sexual dysfunction caused by diabetes. Counseling can help individuals and couples to identify and address any psychological factors that may be contributing to their sexual dysfunction. Couples therapy can also be useful for improving communication and intimacy between partners.
Diabetes can have a significant impact on sexual health in both men and women. High blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage, vascular damage, and hormonal imbalances that can cause sexual dysfunction. Erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, decreased sexual desire, difficulty achieving sexual arousal, and vaginal dryness are all common sexual dysfunctions caused by diabetes. However, there are several treatment options available for individuals with sexual health conditions and diabetes. Medications, hormone replacement therapy, vaginal lubricants, and counseling and therapy can all be effective treatments for sexual dysfunction caused by diabetes.
Complication’s With Diabetes
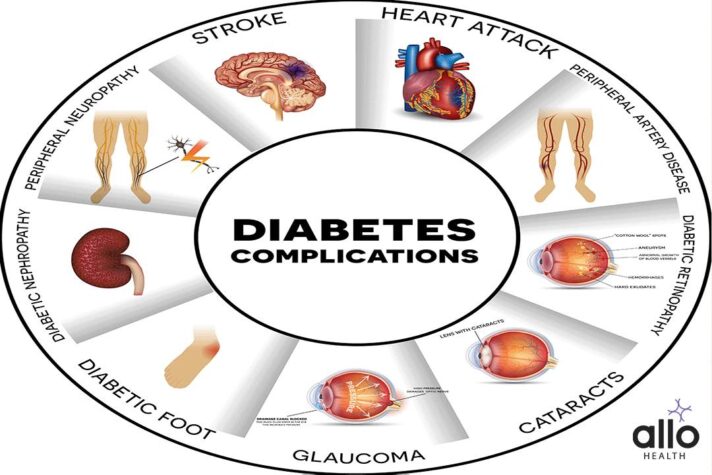
Cardiovascular disease: Diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Neuropathy: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves throughout the body, leading to numbness, tingling, and even pain in the hands and feet.
Nephropathy: Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or even kidney failure.
Retinopathy: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems and even blindness.
Foot complications: Nerve damage and poor circulation in the feet can lead to foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation.
Skin complications: Diabetes can lead to skin infections, dryness, and slow healing of wounds.
Hearing loss: People with diabetes are more likely to experience hearing loss.
Cognitive impairment: Diabetes has been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Gastroparesis: Diabetes can damage the nerves that control the stomach, leading to delayed digestion and other gastrointestinal problems.
Increased risk of infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making it harder to fight off infections.
Types Of Diabetes Treatment
There are several types of diabetes treatment, which may include lifestyle changes, oral medications, injectable medications, and insulin therapy. The specific treatment plan will depend on the type of diabetes a person has, as well as their individual needs and circumstances. Here are some common types of diabetes treatment:
Lifestyle changes: This includes maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. These changes can help manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
Oral medications: For people with type 2 diabetes, oral medications may be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels. These medications work by increasing insulin production or sensitivity, or by slowing down the absorption of glucose in the intestine.
Injectable medications: Injectable medications may be used for people with type 2 diabetes who do not respond to oral medications. These medications include GLP-1 receptor agonists, which help stimulate insulin production and reduce glucose production in the liver, and SGLT2 inhibitors, which help reduce glucose reabsorption in the kidneys.
Insulin therapy: Insulin therapy may be necessary for people with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who do not respond to other treatments. Insulin is typically injected under the skin using a syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. There are different types of insulin, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin, which can be used alone or in combination.
Bariatric surgery: For people with severe obesity and type 2 diabetes, bariatric surgery may be an option. This surgery can help improve blood sugar control and reduce the need for diabetes medication.






































