Understanding the Anatomy and Function of the Penis

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr. Aswathi P T earned her MBBS degree and completed her internship at Government Medical College, Kozhikode, and possess diverse professional background spanning 3.5 years. Her experience includes a wide range of healthcare settings, including health centers, hospitals, and teleconsultation services.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 16 June, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
The penis plays a crucial role in both reproduction and sexual pleasure. Understanding how it works and how to maintain its health is important for every man.
Let’s take a detailed look at the anatomy and function of the penis, as well as common health issues and lifestyle factors that can affect its performance.
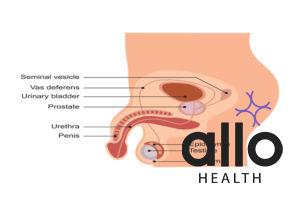
The Structure of the Penis
The human penis is an external organ of male reproductive system responsible for urination and sexual intercourse. It consists of several anatomical structures that play essential roles in its functions. Here’s an explanation of the structure of the penis:
Spongy Tissue (Corpus Spongiosum and Corpus Cavernosum): The penis contains two cylindrical columns of erectile tissue called the corpus cavernosum (plural: corpora cavernosa) and a single column of erectile tissue called the corpus spongiosum. These erectile tissues are responsible for the penis becoming erect during sexual arousal. They fill with blood, causing the penis to enlarge and become rigid.
Fold of Skin (Prepuce or Foreskin): The fold of skin that covers the glans penis is called the prepuce or foreskin. In some males, the foreskin may be removed in a procedure called circumcision.
Connective Tissue: The penis is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue that helps support and protect its internal structures.
Glans Penis: The glans penis, also known as the head of the penis, is a sensitive and bulbous structure located at the tip of the penis. It is richly innervated and plays a crucial role in sexual pleasure and stimulation.
Sac of Skin (Scrotum): The scrotum is a sac of skin that houses the testes, which are responsible for sperm production. The scrotum helps regulate the temperature of the testes to maintain optimal sperm production conditions.
Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s Glands): These small glands are located beneath the prostate gland. During sexual arousal, they secrete a clear fluid that helps lubricate and neutralize the acidity of the urethra before the passage of semen during ejaculation.
Prostate Gland: The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland situated just below the bladder and surrounding the urethra. It secretes a milky fluid that makes up a significant portion of semen, providing nutrients and protecting sperm during ejaculation.
The penis may naturally have a slight downward curve when erect, which is entirely normal and varies among individuals.
The appearance and size of the penis can vary among individuals, and there is a wide range of normal variations.
Interestingly, the size of the penis can vary greatly among individuals. The average erect penis size is around 5.16 inches (13.12 cm). The size can range from as small as 1.6 inches (4 cm) to as large as 10.2 inches (26 cm). Remember, size does not necessarily correlate with sexual pleasure or satisfaction.
If you have concerns about the structure or function of your penis, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a urologist for proper evaluation and advice.
The penis can experience a variety of medical conditions, such as erectile dysfunction, Peyronie’s disease, and priapism. These conditions can affect a man’s sexual health and may require medical treatment.
The Role of the Penis in Reproduction
The primary function of the penis is to deliver sperm into the female reproductive system. During sexual intercourse, the penis becomes erect and releases semen, which contains sperm, into the vagina. From there, the sperm travel towards the fallopian tubes, where they may fertilize an egg.
However, the penis also plays a role in sexual pleasure and arousal. The penis contains numerous nerve endings that can be stimulated during sexual activity, leading to feelings of pleasure and orgasm. The penis can also play a role in bonding and intimacy between sexual partners.
Not all individuals with a penis are able to produce sperm or impregnate a partner. Some may have medical conditions or have undergone procedures that affect their fertility.
Practice safe sex to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted infections, which can have negative effects on reproductive health.
Common Penis-Related Health Issues and Their Causes
There are several health issues and clinical conditions that can affect the penis:
- Erectile dysfunction: Erectile dysfunction is a common condition that can be caused by physical factors such as cardiovascular disease or psychological factors such as anxiety.
- Peyronie’s disease: Peyronie’s disease is characterized by the development of scar tissue in the penis, which can cause pain during erections.
- Priapism: Priapism is a condition in which the penis remains erect persisting beyond or without sexual stimulation, for an extended period of time, causing pain and potential damage to the tissue. If the erection lasts for more than 4 hours, it’s a medical emergency.
- Paraphimosis: This is an acute condition where the foreskin of the penis becomes trapped behind the glans and cannot be pulled back to its original position. It is a painful condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
Practicing safe sex can also help prevent certain penis-related health issues. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea and chlamydia can cause inflammation and damage to the penis, leading to long-term health problems.
Using condoms and getting regular STI testing can help reduce the risk of contracting these infections and protect overall penis health.
How to Maintain Good Penile Health
Maintaining good penile health involves a combination of healthy lifestyle choices and regular medical checkups. Some health practices:
- Staying physically active
- Eating a balanced diet
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Practice safe sex
- Regular checkups with a healthcare provider can also help to identify and treat any problems early on.
- Keep the genital area/penile skin clean and dry to prevent infections.
- Regularly washing with mild soap and water, and drying thoroughly afterwards, can help to prevent bacterial and fungal infections.
- Wearing clean, breathable underwear and avoiding tight-fitting clothing can also help to prevent moisture buildup and reduce the risk of infections.
If any unusual symptoms or changes in the genital area occur, such as swelling, itching, redness, or discharge, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
Psychological Factors That Can Affect Penile Function
Mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and stress can have a significant impact on a man’s ability to achieve and maintain an erection. Seeking support from a mental health professional and practicing mindfulness techniques can help to alleviate these symptoms and improve sexual function.
Another psychological factor that can affect penile function is performance anxiety. Men who are worried about their sexual performance or feel pressure to perform may experience difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
Communication with a partner, setting realistic expectations, and focusing on pleasure rather than performance can help to reduce anxiety and improve sexual function.
Past traumatic experiences such as sexual abuse or assault can also impact penile function. Men who have experienced trauma to seek support from a mental health professional and to communicate with their partner about their needs and boundaries. With the right support and care, it is possible to overcome the effects of trauma and improve sexual function.
The Relationship Between Age and Penis Function
As men age, their hormone levels and physical health may decline, leading to a decline in sexual function. However, there are many ways to maintain sexual health as you age, such as staying active and engaging in regular sexual activity.
One of the most common causes of erectile dysfunction in older men is cardiovascular disease. This is because the blood vessels that supply blood to the penis can become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow and making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
To reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking.
The Effects of Lifestyle Choices on Penile Health
Lifestyle choices such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can have a negative impact on penile health. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding high blood pressure can also help to prevent erectile dysfunction and other related health issues.
Regular physical activity can improve blood flow and overall cardiovascular health, which can in turn improve erectile function. On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity and other health issues that can lead to erectile dysfunction.
Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure and other health problems that can affect erectile function.
The Link Between Diet and Erectile Dysfunction

Certain foods and dietary habits can contribute to erectile dysfunction, such as a diet high in fat and processed foods. Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet, as well as avoiding excessive sugar and caffeine, can help to improve overall sexual health.
In addition to diet, regular exercise can also play a role in preventing erectile dysfunction. Exercise helps to improve blood flow and circulation, which is essential for healthy sexual function. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, most days of the week.
Certain medications and medical conditions can contribute to erectile dysfunction. If you are experiencing persistent issues, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and explore potential treatment options.
How to Talk to Your Partner About Sexual Health Concerns
Open communication with your partner is key to maintaining a healthy and fulfilling sexual relationship. Discussing concerns or seeking advice from a healthcare professional can help to address any issues and improve sexual function.
Sexual health concerns are common and nothing to be ashamed of. By talking openly with your partner, you can work together to find solutions and support each other through any challenges. Remember to approach the conversation with empathy and understanding, and to listen actively to your partner’s concerns as well.
Understanding the Importance of Safe Sex Practices
Practicing safe sex is important for preventing sexually transmitted infections and unwanted pregnancy. Using condoms, getting regular STI testing, and discussing sexual history with your partner are all important steps in maintaining sexual health.
Safe sex practices can vary depending on the type of sexual activity. For example, Dental dams (latex or polyurethane sheets) can be used during oral sex to reduce the risk of STIs, and lubrication can be used during vaginal or anal sex to prevent tears and discomfort. It is important to educate yourself on the different methods of safe sex and to communicate with your partner to ensure that both parties are comfortable and protected.
Key Takeaways:
- The penis is an external male reproductive organ responsible for reproduction and sexual pleasure.
- It consists of spongy tissue (corpus spongiosum and corpora cavernosa) that becomes erect during sexual arousal.
- The penis has a fold of skin called the prepuce or foreskin, and a glans penis at the tip.
- The scrotum houses the testes, responsible for sperm production, and the prostate gland secretes fluids that form part of semen.
- Common penis-related health issues include erectile dysfunction, Peyronie’s disease, priapism, and paraphimosis.
- Factors affecting penile health include lifestyle choices, psychological factors, age, and diet. Open communication with a partner and practicing safe sex are crucial for sexual health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is an uncircumcised penis?
A: It is a penis that has not undergone the surgical removal of the foreskin, which is a fold of skin that covers the glans penis.
Q: What is the root of the penis?
A: The root of the penis refers to the base or attached part of the penis, which is located internally and anchored to the pelvic bones. It contains three erectile tissues and two muscles It includes the portion of the penis that connects to the pelvic floor muscles and structures within the body.
Q: What congenital conditions cause abnormal penile formation?
A: Congenital conditions that cause abnormal penile formation include hypospadias, where the urethral opening is on the underside of the penis instead of at the tip, and epispadias– urethra opening is on the upper side of the penis.
Q: What minor conditions can cause penis pain?
A: Minor conditions that can cause penis pain include urinary tract infections (UTIs) and irritation or inflammation of the penile skin, such as balanitis (inflammation of the glans), balanoposthitis (inflammation of both prepuce and glans penis) or dermatitis.






































