Female Reproductive System

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

A Psychotherapist with Clinical specialization, working for over seven years now. Areas of specialization range from Anxiety-related disorders, Mood-related disorders, Personality disorders, Sexual dysfunctions & other mental health issues.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 10 November, 2023
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
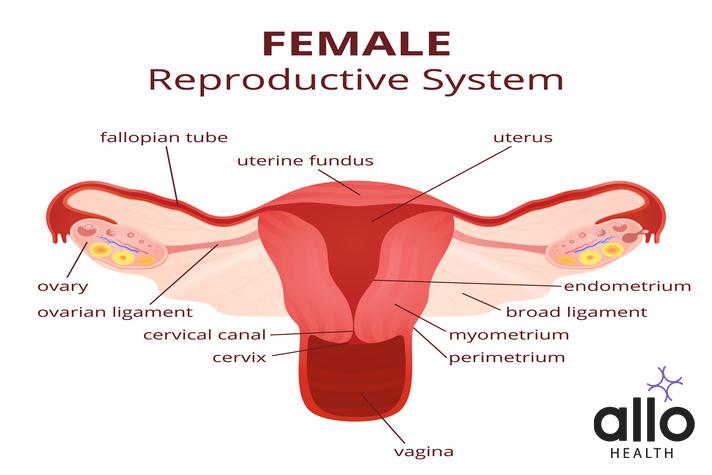
The female reproductive system is a complex and sophisticated system that is responsible for various functions such as the production of eggs, the regulation of hormones, and the support of pregnancy. This system plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and fertility of women and is made up of several key components, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
What Organs Are Part Of The Female Reproductive System?
External Organs
The external female reproductive organs refer to the vulva which includes the mons pubis, the labia majora, the labia minora, the clitoris, and the Bartholin’s glands. The external female reproductive organs play a crucial role in human reproduction.
Vulva
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia and includes all the external organs. The mons pubis is a fatty area located above the pubic bone, covered by pubic hair. The vulva protects the internal reproductive organs from external damage and provides a moist environment that helps to maintain the health of the internal organs.
Labia – Majora and Minora
The labia majora are two thick, fleshy folds of skin that protect the other external genital organs. The labia minora are two thin folds of skin that lie inside the labia majora and surround the vaginal opening.
Clitoris
The clitoris is a small, highly sensitive organ located at the top front of the vulva, which plays an important role in sexual stimulation. The clitoris, as mentioned earlier, plays a crucial role in sexual stimulation, which is important for overall sexual pleasure in some women.
Bartholin’s Glands
The Bartholin’s glands are located on either side of the vaginal opening and secrete a lubricating fluid during sexual arousal. The Bartholin’s glands secrete a lubricating fluid during sexual arousal, which helps to reduce friction and discomfort during sexual intercourse and increases the chances of fertilization.
The external organs of the female reproductive system play a vital role in human reproduction. They protect the internal reproductive organs, play a role in sexual stimulation, and secrete a lubricating fluid to increase the chances of fertilization. It is important to maintain the health of these organs to ensure the proper functioning of the female reproductive system and increase the chances of conception. Regular gynecological check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help to keep the external female reproductive organs in good health.
Internal Organs
The female reproductive system is composed of several internal organs, each with its own specific functions, that work together to facilitate conception, pregnancy, and birth.
Ovaries
The ovaries are the primary reproductive organs in the female body. They produce and release eggs, also known as ova, into the fallopian tubes, where fertilization may occur. The ovaries also produce hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and contribute to the development of secondary sexual characteristics, such as breast growth and a wider pelvis.
Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes are the pathways that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They are lined with tiny, finger-like projections called fimbriae that help to sweep the eggs towards the uterus. If an egg is fertilized by a sperm, it will typically occur within the fallopian tubes, where the fertilized egg then begins its journey towards the uterus.
Uterus
The uterus, also known as the womb, is a muscular and pear-shaped organ that is responsible for nurturing and supporting the developing fetus. It is comprised of three layers of tissue: the endometrium, myometrium, and perimetrium. The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, which thickens and sheds every month during menstruation. If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg will implant into the endometrium and grow into a fetus.
Cervix
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, connecting it to the vagina. It is composed of strong, flexible muscles that allow it to dilate (open) during childbirth to allow the baby to pass through. The cervix also produces mucus, which helps to protect and nourish the sperm as it travels towards the egg.
Vagina
The vagina is a muscular canal that connects the uterus to the outside of the body. It is the birth canal through which the baby passes during childbirth and is also the place where sexual intercourse occurs. The vagina is also an important part of the female reproductive system as it is where menstrual blood exits the body during menstruation.
What Does The Female Reproductive System Do?
The female reproductive system is a complex system made up of various organs and tissues that work together to perform a range of functions necessary for human reproduction. These functions can be broadly categorized into three main areas: production of eggs, provision of a supportive environment for the fertilized egg, and childbirth.
Ovulation
Egg production, also known as ovulation, is the first and foremost function of the female reproductive system. The process begins in the ovaries, where eggs are stored and mature. When a woman reaches puberty, her ovaries release a mature egg each month, which then travels through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus. If the egg is fertilized by sperm, it implants into the uterus and begins the process of pregnancy.
Fertilization
The uterus provides a supportive environment for the fertilized egg to grow and develop. This vital organ has a rich blood supply and muscular walls that can expand and contract to accommodate the growing fetus. Additionally, the uterus is lined with a special type of tissue called the endometrium, which thickens and prepares for implantation of the fertilized egg.
Childbirth
Childbirth is the final function of the female reproductive system. When the time comes for the baby to be born, the uterus contracts and pushes the baby out through the vagina. This process is facilitated by hormones, including oxytocin, which stimulates uterine contractions, and prostaglandins, which soften the cervix and stimulate labor.
Menstrual Cycle
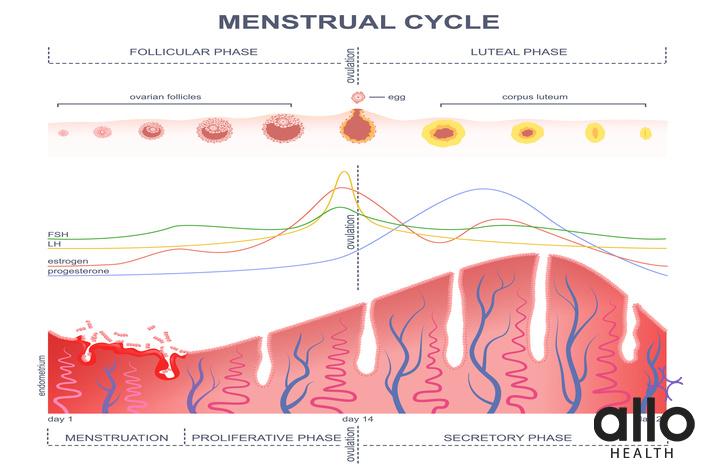
The menstrual cycle is a regular natural process that occurs in fertile women, characterized by physiological changes in the reproductive system. This cycle prepares the female body for pregnancy and is critical for reproductive health. In this essay, we will explore the menstrual cycle in detail, including its stages, hormones involved, and the common concerns associated with it.
The menstrual cycle typically lasts for 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days. It is divided into three stages: the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
Follicular Phase
The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts for approximately 14 days. During this stage, the body prepares for ovulation by increasing levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones cause the growth of a follicle in the ovary, which contains an egg.
Ovulatory Phase
Ovulation occurs around the 14th day of the menstrual cycle, when the mature follicle ruptures, releasing the egg into the fallopian tube. This is the time when a woman is most fertile, and if the egg is fertilized, it can lead to pregnancy.
Luteal Phase
The luteal phase begins after ovulation and lasts for approximately 14 days. During this stage, the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone, a hormone essential for pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum will dissolve, causing a decline in progesterone levels and leading to menstruation.
The menstrual cycle is regulated by several hormones, including FSH, LH, progesterone and estrogen levels. These hormones interact with each other to create a complex feedback system that controls the cycle. Hormonal imbalances can cause concerns such as irregular cycles, heavy bleeding, and premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
The female reproductive system contains a limited number of eggs, also known as ova or oocytes. These eggs play a crucial role in fertility and the ability to conceive.
It is estimated that a female is born with approximately 1 to 2 million eggs in her ovaries. However, this number decreases rapidly as she reaches puberty, and by the time she is ready to conceive, only about 400 to 500 eggs remain. As a woman ages, the number of eggs continues to decrease, leading to a decline in fertility.
The female reproductive system is regulated by a delicate balance of hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Estrogen, produced by the ovaries, regulates the menstrual cycle and plays a role in maintaining bone health and sexual function. Progesterone, also produced by the ovaries, helps to prepare the uterus for pregnancy and supports the development of the fetus during pregnancy. FSH, produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries and helps to regulate the menstrual cycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
(1) What is the female reproductive system?
The female reproductive system is a complex network of organs and structures responsible for producing and transporting eggs, supporting fertilization, nurturing a developing fetus, and giving birth. It includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
(2) What are the primary functions of the ovaries?
The ovaries are responsible for producing and releasing eggs (ova) during the menstrual cycle. They also produce hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and play a role in maintaining reproductive health.
(3) What is the function of the fallopian tubes?
The fallopian tubes are thin, tube-like structures that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They provide a pathway for the released egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus. Fertilization of the egg by sperm typically occurs in the fallopian tubes.
(4) What is the uterus?
The uterus, also known as the womb, is a muscular organ where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus during pregnancy. It undergoes monthly changes in response to hormonal fluctuations, shedding its lining during menstruation if pregnancy does not occur.
(5) What is the cervix?
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It has a small opening called the cervical os, which allows the passage of menstrual blood and serves as the entrance for sperm to enter the uterus during intercourse. During childbirth, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through.
(6) What is the vagina?
The vagina is a muscular canal that connects the cervix to the external genitalia. It serves as the birth canal during childbirth and also allows for the insertion of the penis during sexual intercourse. The vagina has a self-cleaning mechanism and produces lubrication for comfortable intercourse.
(7) What is menstruation?
Menstruation, or the menstrual cycle, is a monthly process where the lining of the uterus is shed if pregnancy does not occur. It involves the release of hormones, the maturation and release of an egg, and the shedding of the uterine lining, resulting in vaginal bleeding.
(8) What is menopause?
Menopause is a natural process that occurs in middle-aged women, typically between the ages of 45 and 55. It marks the end of reproductive years and is characterized by the cessation of menstruation and a decline in hormone production. Women may experience various symptoms, such as hot flashes and mood changes.
(9) What is breast development and its significance?
Breast development is a normal part of female puberty. It involves the growth and enlargement of the breasts due to hormonal changes. Breasts play a crucial role in breastfeeding and are composed of glandular tissue and fatty tissue.
(10) What are common disorders of the female reproductive system?
Common disorders include menstrual irregularities, such as dysmenorrhea (painful periods) and amenorrhea (absence of periods); infections like yeast infections and urinary tract infections; sexually transmitted infections; and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and uterine fibroids. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are essential for maintaining reproductive health.
(11) What is the importance of Kegel exercises for the female reproductive system?
Kegel exercises involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles, which can help strengthen the muscles that support the uterus, bladder, and bowel. These exercises are often recommended to improve urinary incontinence, support pelvic organ health, and enhance sexual satisfaction.
(12) What are some common cultural practices or beliefs related to the female reproductive system?
Cultural practices such as Ayurveda and traditional medicine are often followed for women’s reproductive health. Additionally, practices like the application of henna during pregnancy, postpartum confinement periods (such as “sutra” or “sutika”), and specific dietary practices are also commonly observed.
(13) What are the traditional contraceptive methods used in India?
In addition to modern contraceptive methods, some traditional contraceptive methods used in India include the use of herbs, such as neem, as a natural contraceptive, and the practice of coitus interruptus (withdrawal method). It’s important to note that modern contraceptive methods are generally more reliable and effective.
(14) What are the cultural beliefs and practices surrounding menstruation?
Menstruation is often associated with cultural beliefs and practices. Menstruating women may be subject to restrictions, such as not entering temples or participating in religious ceremonies. However, there is a growing movement in India to challenge these taboos and promote menstrual hygiene awareness and education.
(15) What are some common reproductive health concerns faced by women in India?
Women in India commonly face reproductive health concerns such as menstrual disorders, including heavy or irregular periods; reproductive tract infections; cervical cancer; and anemia due to inadequate nutrition. Access to quality healthcare, education, and awareness programs can help address these concerns.
(16) What are the available resources for reproductive health information and services in India?
In India, various resources are available for reproductive health information and services. Government initiatives like the National Health Mission provide reproductive healthcare services. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community health centers, and clinics also play a significant role in providing reproductive health information and services.
(17) What is the significance of prenatal care>
Prenatal care is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and reducing the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Regular check-ups, proper nutrition, vaccinations, and monitoring of fetal development are important aspects of prenatal care.
(18) What are some traditional postpartum care practices?
Traditional postpartum care practices vary across different regions. Practices such as “japa” (a period of confinement), massage, and dietary restrictions are common. However, it is important to strike a balance between traditional practices and evidence-based postpartum care to ensure the health and well-being of the mother and newborn.
(19) What are the available resources for infertility treatment in India?
India has various infertility treatment centers and clinics that offer a range of services, including assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), and fertility medications. It is advisable to consult with a qualified fertility specialist for personalized guidance and treatment options.
Female reproductive system is a complex and vital system that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and fertility of women. Understanding the components and functions of this system is important for maintaining reproductive health and for addressing any concerns that may arise. Regular visits to a healthcare provider and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help to ensure the continued health of the female reproductive system.







































