What Is A Vasectomy And Tubectomy?

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr. Aditi completed her undergraduate medical education at AJIMS, Mangalore, after which she worked in multi-speciality hospitals with COVID patients and in the Pain and Palliative medicine department. Driven by her experiences, she developed a keen interest in psychiatry. Dr. Aditi believes that mental health is just as, if not more important, than physical health.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 02 January, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
"The following blog article may discuss medical treatments and interventions. However, it is important to note that the information provided is for general educational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional for personalized medical advice.
Book consultation
Medical treatments are complex and should be tailored to individual circumstances. The information presented in this blog may not be applicable to everyone, as each person's medical condition, history, and needs are unique. Only a qualified healthcare professional can evaluate your specific medical situation, consider relevant factors, and provide appropriate recommendations for diagnosis, treatment options, and monitoring.
It is crucial to note that self-diagnosis, self-medication, or relying solely on the information provided in this blog for treatment decisions can have serious health consequences. "
There are several methods of birth control available today, including condoms, pills, and implants. Two of the most popular permanent sterilization techniques for couples who don’t want children are vasectomy and tubectomy. Both methods involve surgical procedures that are designed to prevent pregnancy for the rest of a person’s life. Before you decide to go for sterilization, there are some important things that you need to know – so let’s define vasectomy and tubectomy.
What Are Sterilization Techniques?
Sterilization techniques for couples are permanent methods of contraception designed to prevent pregnancy by surgically blocking or sealing the reproductive pathways. These methods are intended for couples who have decided not to have any more children. The two primary sterilization techniques for couples are tubal ligation (female sterilization) and vasectomy (male sterilization).
Difference Between Vasectomy And Tubectomy
Vasectomy and tubectomy are two different surgical procedures that involve sterilization to prevent pregnancy. They are permanent methods of contraception intended for individuals or couples who have decided not to have any more children. Here are the details of the differences between vasectomy and tubectomy:
Vasectomy
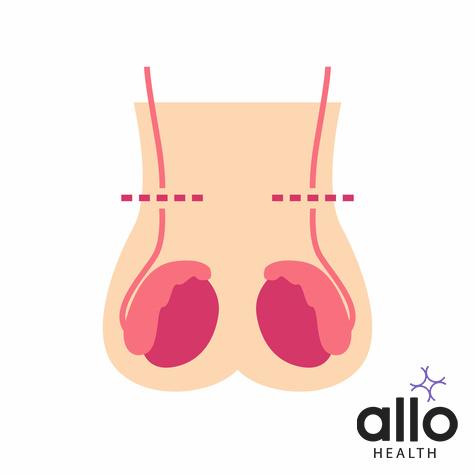
A vasectomy is a surgical procedure for male sterilization. It involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the urethra. By blocking the passage of sperm, a vasectomy prevents sperm from mixing with semen during ejaculation, thus making a man sterile.
Procedure:
- The scrotum is cleaned and numbed with a local anesthetic.
- A small incision is made on each side of the scrotum to access the vas deferens.
- The vas deferens is cut, and a section may be removed. Sometimes, the cut ends are sealed or cauterized.
- The cut ends are then either tied, clipped, stitched, or sealed with a medical adhesive to prevent the sperm from passing through.
- The incisions are closed with stitches or adhesive, and the procedure is completed.
Advantages:
- Vasectomy is a relatively quick and simple procedure.
- Recovery time is generally shorter compared to tubectomy.
- There is usually less discomfort and fewer potential complications.
Limitations:
- It takes some time (several weeks or ejaculations) after the procedure to clear any remaining sperm from the vas deferens, so backup contraception is needed until confirmed sperm absence.
- The procedure is generally irreversible, although vasectomy reversal is possible in some cases but may not always result in successful fertility restoration.
Tubectomy
Tubectomy, also known as tubal ligation or female sterilization, is a surgical procedure for female sterilization. It involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes, which are responsible for carrying eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Blocking the fallopian tubes prevents eggs from meeting sperm, thereby preventing fertilization.
Procedure:
- Anesthesia is administered, often through general anesthesia.
- Small incisions are made in the abdomen, typically near the navel.
- The fallopian tubes are located and either blocked, cut, sealed, or tied off to prevent the eggs from traveling to the uterus.
- The incisions are closed using stitches or sutures, and the procedure is completed.
Advantages:
- Tubectomy offers long-term contraception without the need for daily interventions.
- It does not affect sexual function or hormone levels.
- Once the procedure is done, there is no need for further contraception.
Limitations:
- Tubectomy is a more invasive procedure compared to vasectomy, with a longer recovery time.
- There is a slightly higher risk of complications compared to vasectomy due to the nature of abdominal surgery.
- Tubectomy is considered permanent and is generally more difficult to reverse.
Vasectomy: Advantages And Disadvantages

Advantages
- Permanent Contraception: Vasectomy is a permanent method of contraception, providing long-term fertility control for men who have completed their desired family size.
- Highly Effective: Vasectomy is highly effective in preventing pregnancy. After the procedure, the risk of impregnating a partner is very low, but it’s important to note that there is still a period of time (several weeks or ejaculations) required for any residual sperm to be cleared from the vas deferens.
- Non-Hormonal: Vasectomy does not affect hormone levels or sexual function. It only prevents sperm from mixing with semen during ejaculation, ensuring that fertilization cannot occur.
- Simple Procedure: The procedure is relatively simple and can often be done on an outpatient basis. It usually takes less than 30 minutes to perform, making it a convenient option for many men.
- Minimal Downtime: Recovery time is generally shorter compared to female sterilization procedures like tubal ligation. Most men can return to work and normal activities within a few days.
- Cost-Effective: Vasectomy is often more cost-effective in the long run compared to other forms of contraception, such as birth control pills or condoms, which need to be continuously purchased.
- Reduced Risk of Certain Cancers: Some studies suggest that vasectomy may be associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer. More research is needed to fully establish this relationship.
Disadvantages
- Irreversible: Vasectomy is considered a permanent procedure, and while vasectomy reversal is possible in some cases, it may not always result in restored fertility. Reversal success rates are generally higher if the reversal is done soon after the original vasectomy.
- Requires Time for Sperm Clearance: After the procedure, there is a period of time required (several weeks or ejaculations) for the remaining sperm to be cleared from the vas deferens. During this time, alternative forms of contraception must be used to avoid unintended pregnancy.
- Surgical Risks: Like any surgical procedure, there is a small risk of infection, bleeding, and complications related to anesthesia. These risks are generally low.
- Psychological Impact: Some men may experience emotional or psychological concerns after the procedure, particularly if they have concerns about their fertility or masculinity. Proper counseling and education can help address these concerns.
- Doesn’t Protect Against STDs: Vasectomy does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Condoms or other barrier methods are still necessary for protection against STDs.
- Cost for Reversal: If a man chooses to undergo a vasectomy reversal, the procedure can be more complex and expensive, and success is not guaranteed.
- Partner’s Concerns: Sometimes, a partner may have concerns or reservations about the permanence of the procedure, which should be discussed and addressed before making a decision.
It’s important for individuals and couples to thoroughly discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and potential consequences of vasectomy with a healthcare professional before making a decision. A thorough understanding of the procedure, its implications, and possible alternatives will help individuals make informed choices about their reproductive health.
Tubectomy: Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages
- Permanent Contraception: Tubectomy is a permanent method of contraception for women who have completed their desired family size. It provides long-term fertility control.
- Highly Effective: Tubectomy is highly effective in preventing pregnancy. Once the fallopian tubes are blocked or sealed, the chances of an egg meeting sperm are virtually eliminated.
- Non-Hormonal: Tubectomy does not affect hormone levels, menstrual cycle, or sexual function. It simply prevents the eggs from reaching the uterus and therefore cannot be fertilized.
- Long-Term Convenience: After the procedure, there is no need for any additional contraception. Women can have peace of mind knowing that they are protected against unintended pregnancy.
- No Interference with Hormones: Unlike some other methods of contraception that involve hormones (such as birth control pills or hormonal IUDs), tubectomy does not interfere with natural hormonal processes.
- Reduced Risk of Certain Cancers: Some research suggests that tubal ligation may be associated with a reduced risk of ovarian cancer. More research is needed to establish this relationship.
- Lower Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy: Since tubectomy prevents the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus, it significantly lowers the risk of ectopic pregnancy, which is a potentially life-threatening condition where the embryo implants outside the uterus.
Disadvantages
- Permanent and Irreversible: Tubectomy is considered a permanent procedure. While some attempts at reversal (tubal ligation reversal) can be made, success rates vary, and it may not always result in restored fertility.
- Surgical Procedure: Tubectomy is a surgical procedure that involves making incisions in the abdomen to access and block the fallopian tubes. Like any surgery, there is a risk of infection, bleeding, and complications related to anesthesia.
- Recovery Time: Recovery time after tubectomy is longer compared to some other contraceptive methods. It may take a few days to a week for women to fully recover.
- Psychological Impact: Some women may experience emotional or psychological concerns after the procedure, particularly if they have concerns about their fertility or body image. Proper counseling and education can help address these concerns.
- Possible Surgical Complications: As with any surgical procedure, there is a small risk of complications, including infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding structures.
- Cost and Availability: Depending on the healthcare system and location, tubectomy procedures may have associated costs. Additionally, access to the procedure may be limited in some areas.
- Doesn’t Protect Against STDs: Tubectomy does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Barrier methods like condoms are still necessary for protection against STDs.
- Partner’s Concerns: Sometimes, a partner may have concerns or reservations about the permanence of the procedure, which should be discussed and addressed before making a decision.
Before opting for tubectomy, individuals and couples should have a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional to fully understand the advantages, disadvantages, and implications of the procedure. Understanding the procedure’s impact on fertility, health, and overall well-being is crucial for making an informed decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
(1) What is Vasectomy?
Vasectomy is a surgical procedure for men that involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, the tubes that transport sperm from the testes to the penis. This blocks the release of sperm during ejaculation, effectively preventing pregnancy. It’s a permanent form of contraception.
(2) What is Tubectomy?
Tubectomy, also known as tubal ligation, is a surgical procedure for women. It involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes, which prevents eggs from reaching the uterus and being fertilized by sperm. Tubectomy is also a permanent method of contraception.
(3) Are These Methods Reversible?
Vasectomy is usually considered irreversible, but there’s a procedure called vasectomy reversal. But, success isn’t guaranteed. Tubectomy is also permanent, with a limited possibility of reversal through tubal ligation reversal surgery.
(4) How Effective Are These Procedures?
Both vasectomy and tubectomy are highly effective. Once the procedures are complete, the risk of pregnancy is significantly reduced. Backup contraception is needed immediately after surgery until confirmed sterility.
(5) Do These Procedures Affect Hormones or Sexuality?
No, both methods do not affect hormone levels or sexual function. Hormones are not altered, and libido remains unaffected.
(6) What Are the Risks of the Procedures?
Both procedures have standard surgical risks such as infection, bleeding, and anesthesia-related complications. Serious complications are rare.
(7) Is There Downtime After the Procedures?
Recovery is generally quicker for vasectomy compared to tubectomy. Most men can resume normal activities within a few days after vasectomy, while women may need a week or more to recover after tubectomy.
(8) Do These Methods Protect Against STDs?
No, neither vasectomy nor tubectomy offers protection against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Barrier methods like condoms are recommended for STD prevention.
(9) Can I Still Ejaculate After Vasectomy?
Yes, you can still ejaculate after vasectomy. The procedure only blocks the sperm’s pathway, but semen production and ejaculation continue as usual.
(10) How Can I Decide Between Vasectomy and Tubectomy?
The decision depends on personal preferences, medical history, and family planning goals. Discussing options with a healthcare professional and considering factors like recovery time, effectiveness, and permanence can help make an informed choice.