HPV And Liver Health
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection known primarily for its association with cervical cancer risk. Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV 16 and 18, have been implicated in the development of liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer. Understanding the relationship between HPV and liver health is crucial for early detection and prevention strategies. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the impact of HPV on liver health and the implications for public health initiatives aimed at reducing liver-related morbidity and mortality.
The Basics: What Is HPV And How Does It Affect The Liver?
- HPV, or human papillomavirus, is a common virus transmitted through sexual contact.
- It can infect the skin and mucous membranes, causing various health concerns, including genital warts and cervical cancer.
- Certain strains of HPV can also affect the liver, leading to liver disease and cancer.
- Chronic infection with high-risk HPV strains, such as HPV 16 and 18, can increase the risk of liver cancer.
- HPV-related liver cancer often develops over many years, making early detection and treatment essential for better outcomes.
- Vaccination against HPV can help prevent infection and reduce the risk of associated liver complications.
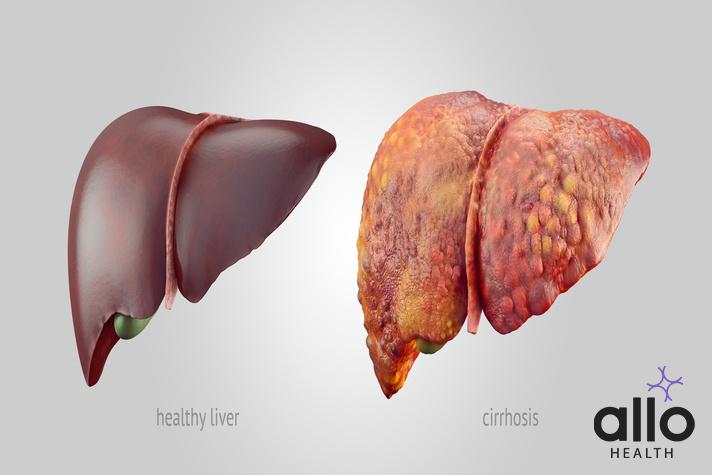
An Overview Of The Different Types Of Liver Diseases Caused By HPV
- Hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses (HBV and HCV) are the primary causes of liver diseases associated with viral infections.
- Chronic hepatitis B and C infections can lead to liver inflammation (hepatitis), cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is not typically associated with liver diseases; it primarily causes genital warts and cervical cancer.
How Is HPV Transmitted And What Are The Risk Factors For Developing Liver Disease?
- HPV, or human papillomavirus, is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
- Skin-to-skin contact with an infected area can also spread HPV.
- Risk factors for developing liver disease include chronic infection with hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus.
- Hepatitis B and C are transmitted through blood and bodily fluids, including unprotected sex and sharing needles.
- Heavy alcohol consumption over time can also increase the risk of liver disease.
- Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and exposure to certain toxins or chemicals.
- Vaccination against HPV and hepatitis viruses can help reduce the risk of infection and liver disease.
Symptoms And Signs Of Liver Diseases Caused By HPV
- Liver diseases caused by HPV (Hepatitis B virus) can manifest with various symptoms and signs.
- Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and abdominal pain.
- Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, may occur in advanced stages.
- Loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting are also common symptoms.
- Some individuals may experience dark urine and pale stools due to impaired liver function.
- Liver diseases caused by HPV can lead to liver inflammation (hepatitis), liver cirrhosis, and liver cancer if left untreated.
- It’s important to seek medical attention if experiencing any of these symptoms, especially in individuals at risk for HPV infection.
Diagnosis And Treatment Options For HPV-Related Liver Conditions
- Diagnosis of HPV-related liver conditions often involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI.
- Specific tests for HPV-related liver conditions may include liver function tests to assess liver enzymes and markers of liver inflammation.
- Biopsy may be performed to confirm the presence of HPV-related liver diseases, such as hepatitis or liver cancer.
- Treatment options for HPV-related liver conditions may include antiviral medications to suppress viral replication, immunomodulatory therapy to reduce inflammation, and targeted therapy or surgery for liver cancer (can also be effective for other human cancers like neck cancers).
- Lifestyle modifications such as avoiding alcohol and maintaining a healthy diet may also be recommended to support liver health.
Prevention Strategies: Vaccinations And Lifestyle Changes To Lower Your Risk
- Stay up-to-date on vaccinations to protect against infectious diseases and lower your risk of illness.
- Follow recommended lifestyle changes to improve overall health and lower disease risk.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean viral proteins to support immune function.
- Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen your body and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Practice good hygiene habits, such as frequent handwashing, to prevent the spread of germs.
- Get enough quality sleep to support immune function and overall well-being.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake to reduce the risk of developing certain health conditions.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and social support to promote immune health.
Debunking Common Myths About HPV And Liver Disease
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus) is not associated with liver disease; it primarily affects the skin and mucous membranes.
- Liver disease is commonly caused by viruses such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C, as well as excessive alcohol consumption and other factors.
- HPV is mainly transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, often during sexual activity.
- Development of liver disease, on the other hand, can result from various factors including viral infections, alcohol abuse, obesity, and certain medications.
- It’s important to understand the distinct causes and risk factors for liver disease, as well as how to prevent and manage it effectively.
The Importance Of Early Detection And Screening For Liver Disease Caused By HPV
- Early detection and screening for liver disease caused by HPV are crucial for timely intervention and improved outcomes.
- HPV (Hepatitis B virus) infection is a leading cause of liver disease, including hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
- Early detection allows for prompt treatment to prevent progression to advanced liver disease or liver cancer.
- Individuals at higher risk, such as those with a history of HPV infection or liver disease, should undergo regular screenings.
- Public health initiatives promoting awareness and screening programs can help reduce the burden of liver disease caused by HPV.
Living with an HPV-Related Liver Disease
- HPV-related liver diseases, such as hepatitis B and C, are caused by infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- These viruses can lead to chronic liver inflammation and damage over time.
- Symptoms of HPV-related liver disease may include fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, and nausea.
- Treatment options for HPV-related liver disease may include antiviral medications, immune modulators, and liver transplants in severe cases.
- Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, and practicing safe sex can help manage the condition.
- Regular monitoring by a health care provider is important to prevent complications and manage symptoms.
Most Asked Questions
-
What is HPV-related liver disease?
HPV-related liver disease refers to liver conditions caused by infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). This includes hepatitis B and C, which can lead to chronic liver inflammation and damage if left untreated.
-
What are the symptoms of HPV-related liver disease?
Symptoms of HPV-related liver disease may include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, there may be no symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease.
-
How is HPV-related liver disease transmitted?
HPV-related liver diseases such as hepatitis B and C are primarily transmitted through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. This can occur through sexual contact, sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, and from mother to child during childbirth.
-
Can HPV-related liver disease be prevented?
Yes, HPV-related liver diseases such as hepatitis B and C can be prevented through vaccination and practicing safe sex. Avoiding sharing needles and other drug paraphernalia can also reduce the risk of transmission.
-
How is HPV-related liver disease treated?
Treatment for HPV-related liver disease depends on the specific condition and its severity. Options may include antiviral medications to suppress the virus, immune modulators to reduce inflammation, and in severe cases, liver transplants. It's important to consult a health care provider for personalized treatment recommendations.