Tick Bite On Penis: How To Identify And Remove

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr.Sushma.V completed MBBS degree from BGS GIMS,bangalore
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 27 December, 2023
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
It’s not uncommon for people to experience tick bites on various parts of their body, including the penis. It’s important to understand that ticks can transmit diseases that can have serious health consequences if left untreated.
What Is A Tick Bite?
A tick bite refers to the act of a tick, a small arachnid parasite, attaching itself to a host’s skin and feeding on its blood. Ticks are ectoparasites, meaning they live on the outer surfaces of their hosts, and they are known for transmitting various diseases to humans and animals through their bites. Understanding the details of a tick bite involves several key aspects:
- Tick Anatomy and Behavior: Ticks have a specialized mouthpart structure called a hypostome that allows them to anchor firmly to their host’s skin. This structure resembles a barbed or serrated harpoon, which aids in secure attachment during feeding. Once a tick has found a suitable host, it uses its hypostome to pierce the skin and insert it into the host’s bloodstream.
- Tick Identification: Ticks come in various sizes, shapes, and colors depending on their species and life stage. They are typically small, ranging from the size of a pinhead to the size of a sesame seed. Ticks have four pairs of legs, which distinguish them from insects that have only three pairs of legs.
- Attachment and Feeding: Ticks locate hosts by detecting cues such as heat, carbon dioxide, and body odor. They often climb vegetation and wait for a host to brush against them, at which point they latch onto the host’s skin. Ticks use their mouthparts to anchor themselves and feed on the host’s blood. Feeding can take several hours to days, during which time the tick will gradually become engorged with blood.
- Disease Transmission: Ticks are notorious for transmitting a range of diseases, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, anaplasmosis, babesiosis, and more. These diseases are caused by various bacteria, viruses, or protozoa present in the tick’s saliva. When a tick feeds on a host, it can introduce these pathogens into the host’s bloodstream, potentially leading to an infection.
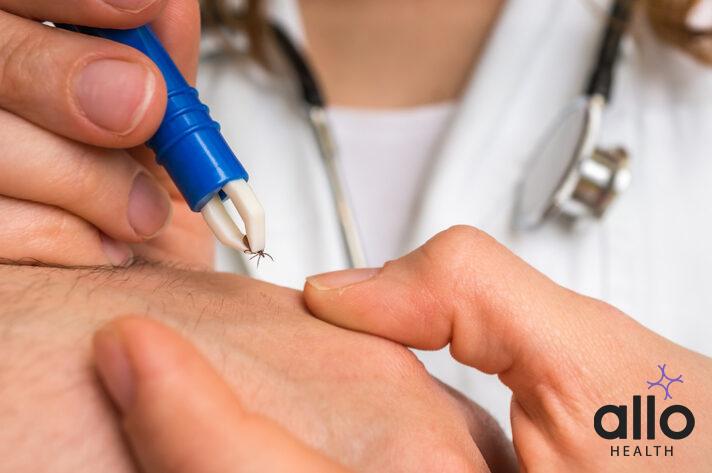
- Tick Removal: Prompt and proper removal of a tick is crucial to reduce the risk of disease transmission. To remove a tick, use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick’s mouthparts as close to the skin’s surface as possible. Gently pull upward with steady, even pressure to avoid squeezing the tick’s body. Do not twist or jerk the tick, as this can cause the mouthparts to break off and remain in the skin. Once the tick is removed, clean the area with soap and water and disinfect the tweezers.
- Preventive Measures: To minimize the risk of tick bites, especially in areas where ticks are prevalent, consider the following measures:
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and tuck pants into socks when outdoors.
- Use insect repellents that are effective against ticks.
- Conduct regular tick checks on yourself, family members, and pets after spending time outdoors.
- Avoid tall grasses and wooded areas if possible.
Symptoms Of A Tick Bite On The Penis
A tick bite on the penis can be concerning and uncomfortable. It’s important to note that the symptoms of a tick bite on the penis are similar to those of tick bites on other parts of the body. Here’s a detailed overview of what you might experience if you have been bitten by a tick on the penis:
- Tick Identification and Location: Ticks can attach to any part of the body, including the penis, if they come into contact with the skin. The first step is to identify the tick and its location on the penis.
- Initial Symptoms: Tick bites are usually painless initially, so you might not notice the tick’s presence right away. Common symptoms might include redness and minor swelling around the bite site.
- Itching and Irritation: As the tick feeds and remains attached, you might start to experience itching, irritation, or a mild burning sensation at the bite site. These symptoms can be particularly uncomfortable in sensitive areas like the penis.
- Engorgement and Appearance: Over time, the tick will become engorged with blood as it feeds. This can cause the tick to appear larger and more noticeable. The area around the bite might become more swollen and reddened due to the tick’s feeding process.
- Potential Infection: If the tick’s mouthparts break off during removal or if you scratch the bite site, there’s a risk of introducing bacteria and causing an infection. Watch for signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, pus, and pain at the bite site.
- Allergic Reactions: In some cases, individuals can develop allergic reactions to tick bites. Symptoms might include severe itching, hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling beyond the bite area. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
- Disease Transmission: Ticks can transmit diseases through their bites, but the risk varies based on the type of tick and the geographical location. Common tick-borne diseases include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and others. If the tick that bit you is known to carry diseases, monitor your health for symptoms such as fever, fatigue, joint pain, and rash.
- Tick Removal: Proper and prompt tick removal is essential to reduce the risk of disease transmission and infection. Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick’s mouthparts as close to the skin’s surface as possible. Gently pull upward with steady, even pressure. Do not twist or jerk the tick. After removal, clean the area with soap and water and disinfect the tweezers.
- Medical Care: If you experience any signs of infection, an allergic reaction, or if you’re unsure about the type of tick and the diseases it might carry, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the situation, provide appropriate treatment, and offer guidance on monitoring for potential complications.
Can A Tick Bite On A Penis Cause Cancer?
Ticks are known for transmitting various diseases, some of which can have serious health implications, but a direct link between tick bites and cancer has not been established.
Cancer is a complex disease that usually develops over time due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Ticks are primarily associated with transmitting infections such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and other bacterial or viral illnesses. While some infections can potentially lead to health complications if left untreated, the development of cancer is not a typical outcome of a tick bite.
If you experience a tick bite on any part of your body, including the penis, and are concerned about potential health risks or infections, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. Healthcare professionals can assess the situation, provide appropriate treatment if needed, and offer guidance on monitoring for any unusual symptoms or complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
(1) Can a tick bite occur on the penis?
Yes, ticks can attach to the skin anywhere on the body, including the penis. Ticks are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide, which the body emits, and can inadvertently latch onto the genital area.
(2) What are the symptoms of a tick bite on the penis?
A tick bite on the penis might cause initial redness, minor swelling, itching, and discomfort. As the tick feeds, the bite area can become more swollen and the tick itself may appear engorged.
(3) How do I remove a tick from my penis?
To remove a tick, use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick’s mouthparts close to the skin’s surface. Gently pull upwards without twisting or jerking. Clean the area with soap and water after removal.
(4) Can a tick bite on the penis lead to infections?
Yes, if the tick’s mouthparts break off during removal or if the bite site is scratched, there’s a risk of introducing bacteria and causing infection. Watch for increased redness, warmth, pus, or pain.
(5) Should I be concerned about diseases from a tick bite on the penis?
There’s a potential risk of tick-borne diseases like Lyme disease, but it depends on the type of tick and region. Watch for symptoms like fever, fatigue, joint pain, and rash. Seek medical help if you’re unsure or experience unusual symptoms.
(6) Can a tick bite on the penis lead to allergic reactions?
Yes, some individuals might develop allergic reactions to tick bites. Symptoms can include severe itching, hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling beyond the bite area. Seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur.
(7) What should I do if I find a tick on my penis?
If you find a tick, use tweezers to remove it carefully. Grasp the tick’s mouthparts near the skin and pull gently. Clean the area after removal. If concerned, monitor for symptoms and consult a doctor.
(8) How can I prevent tick bites on the penis?
Wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, and avoiding tall grass or wooded areas can help prevent tick bites. Regular body checks after outdoor activities can also help in early detection.
(9) How soon should I seek medical help after a tick bite on the penis?
If you experience signs of infection like increasing redness, warmth, pus, or pain, or if you’re uncertain about tick type or diseases it might carry, consult a doctor promptly for assessment and guidance.
(10) Is professional medical help necessary for tick bites on the penis? In most cases, proper tick removal and self-monitoring suffice. If you notice signs of infection, allergic reactions, or uncertainty about the tick’s type, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for peace of mind.






































