Understanding Penile Cysts: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr. Aditi completed her undergraduate medical education at AJIMS, Mangalore, after which she worked in multi-speciality hospitals with COVID patients and in the Pain and Palliative medicine department. Driven by her experiences, she developed a keen interest in psychiatry. Dr. Aditi believes that mental health is just as, if not more important, than physical health.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 18 January, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.

"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
Penile cysts are relatively common and often benign growths that can develop anywhere on the penis. They can range from small bumps to larger, more noticeable growths. This article will cover everything you need about penile cysts, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Are Penile Cysts and Their Types?
Penile cysts are cystic formations that occur on or within the penis. They can develop due to various underlying causes, and their presence can lead to discomfort, concern, or curiosity.
Several types of penile cysts can develop on the penis. These include sebaceous cysts, penile epidermal cysts, epidermoid cysts, epidermal inclusion cysts and median raphe cysts.
Epidermoid Cysts: Epidermoid cysts, also known as epidermal cysts, are common cysts that form beneath the skin’s surface. These cysts develop due to the blockage of hair follicles or oil glands, accumulating keratin and other substances.
The symptoms of epidermoid cysts are small and yellow bumps, redness or inflammation and drainage. The cysts usually develop in the scrotum but can also appear on the penis.
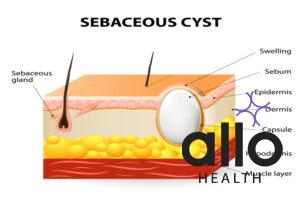
Sebaceous Cysts: Sebaceous cysts, also referred to as epidermal inclusion cysts, become damaged or blocked. The symptoms of sebaceous cysts are drainage and a small lump under the skin. In this condition, the cyst becomes blocked or damaged. These cysts form when oil glands become blocked, causing the accumulation of oil and debris beneath the skin. Sebaceous cysts can vary in size and often feel like small, movable lumps beneath the skin.
Penile Epidermal Inclusion Cysts: Penile epidermal inclusion cysts are a specific type of sebaceous cyst that develops when skin cells become trapped beneath the surface of the skin. They occur as a complication of circumcision. Penile epidermal cysts rarely appear on the penis. The symptoms of a penile epidermal inclusion cyst are a lump that grows larger and is movable underneath the skin.
Median Raphe Cysts: Median raphe cysts can occur anywhere along the genitoperineal raphe from the urethral meatus to the anus. Median raphe cysts are rare cysts that are present at birth. The tissue gets trapped near the median raphe nerve in the penis. The median raphe cysts usually don’t cause any problems. The symptoms include painful urination, swelling and changes in urinary frequency.
What Causes Penile Cysts?
The exact causes of penile cysts are not fully understood. However, it is believed that they may develop due to an obstruction in the skin glands or hair follicles on the penis. Other factors that may increase the risk of developing penile cysts include poor hygiene, trauma to the penis, and certain genetic conditions.
Penile cysts can also be caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as genital herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), and syphilis. These infections can cause inflammation and blockages in the skin glands and hair follicles, leading to the formation of cysts.
In some cases, penile cysts may be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition such as Peyronie’s disease or penile cancer. It is important to seek medical attention if you notice any unusual lumps or bumps on your penis, especially if they are painful or rapidly growing.
What Are the Symptoms of Penile Cysts?
Symptoms of penile cysts can vary based on the type and size of the cyst. Common symptoms include:
- A small, painless lump beneath the skin
- Generally not painful
- They are similar to the color and texture of your skin
- Redness, swelling, or tenderness if the cyst becomes infected
- Discharge of pus or fluid if the cyst ruptures
- STD-related bumps appear as clusters, and they cause some degree of pain
Diagnosis: How to Identify a Penile Cyst
If you suspect that you may have a penile cyst, you should see a healthcare provider because diagnosing penile cysts involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider. Methods of diagnosis may include:
- Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will visually inspect the cyst and may inquire about your medical history.
- Urine Tests: In some cases, urine tests might be conducted to rule out any underlying infections.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify potential underlying conditions or infections.
- Biopsy: If the cyst’s appearance is concerning, a small tissue sample (biopsy) might be taken for further analysis.

- Swab Tests: Swabs may be used to collect samples from the cyst for laboratory testing.
In most cases, penile cysts are harmless and do not cause any complications. However, if left untreated, they can become infected or inflamed, which can cause pain and discomfort. In rare cases, they can also turn cancerous.
It is important to note that penile cysts can also affect sexual function. If a cyst grows large enough, it can cause difficulty with erections or painful intercourse. Additionally, if a cyst is located near the urethra, it can cause urinary problems such as difficulty urinating or frequent urination.
If you notice any changes in your genital area, such as the appearance of a lump or bump, it is important to see a healthcare provider for an evaluation. They can determine if the growth is a cyst or something more serious, and recommend appropriate treatment options to prevent any potential complications.
Is a Penile Cyst Contagious?
No, penile cysts are not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person. If you have STD-related penile bumps, it can spread through sexual contact.
Penile cysts are harmless and do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or pain. However, it is important to consult a healthcare provider if you notice any changes in the size, shape, or colour of the cyst or if you experience any pain or discomfort during sexual activity. Your healthcare provider may recommend further testing or treatment options, such as draining the cyst or surgical removal, depending on the severity of the cyst.
Treatment Options for Penile Cysts
In most cases, treatment is not necessary if you’re experiencing any pain or discomfort follow the below steps:
Keep the Area Clean: Ensuring proper hygiene is essential in preventing infection and promoting the healing of penile cysts. Here’s how to maintain cleanliness:
Gentle Cleaning: Wash the affected area with antibacterial soap and warm water during your daily shower or bath. Avoid using harsh soaps or scrubbing vigorously, as this can irritate the cyst.
Pat Dry: After washing, gently pat the area dry using a clean, soft towel. Avoid rubbing the cyst, as this can lead to irritation.
Apply a Warm and Wet Washcloth:
Applying a warm and wet washcloth to the cyst three to four times a day can help drain the cyst.
Soak a Cloth: Dip a clean washcloth in warm water and wring out excess water.
Apply to the Cyst: Place the warm, wet washcloth over the cyst for 10 to 15 minutes. This can help soften the cyst’s contents and reduce pain or swelling.
Cover the Cyst with a Bandage:
Covering the cyst with a sterile bandage can help protect it from friction, irritation, and potential contamination:
Clean the Area: Before applying the bandage, ensure that the area around the cyst is clean and dry.
Choose a Sterile Bandage: Select a sterile adhesive bandage appropriate for the cyst’s size. Make sure the bandage is large enough to cover the cyst fully.
Surgical Options for Treating Penile Cysts
Treatment options for penile cysts depend on factors such as the cyst’s size, type, and impact on your health. Treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: If the cyst is infected, antibiotics might be prescribed to manage the infection.
- Excision: Surgical removal of the cyst may be recommended, especially if it’s causing discomfort or cosmetic concerns. Surgical excision includes surgical removal of entire cyst that includes the cyst wall.
- Drainage: If the cyst is fluid-filled and causing discomfort, draining the fluid might provide relief.
- Steroid Injections: In cases of inflammation, steroid injections can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
How to Prevent a Cyst in Penis?
Maintaining proper hygiene is fundamental to preventing various skin issues, including penile cysts. Here’s how to practice good hygiene:
- Gentle Cleansing: Wash the genital area with mild soap and lukewarm water during your daily shower. Avoid using strong or scented soaps that can disrupt the natural balance of the skin.
- Thorough Drying: After cleansing, ensure the area is completely dry before putting on clothes. Excess moisture can create a conducive environment for bacterial growth.
Avoiding Extremely Vigorous Sex:
While intimacy is essential for relationships, overly aggressive or rough sexual activities can potentially lead to irritation, abrasions, and even minor injuries that increase the risk of cyst formation.
Using Protection:
Using protection during sexual activity can reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and the potential for cysts that might result from infections or inflammations:
Consistently use condoms during sexual intercourse to lower the risk of STIs and minimize exposure to potential irritants.
Wearing a Protective Cup:
Contact sports can put the genital area at risk of injury, which might contribute to cyst development. To mitigate this risk:
- Protective Cup: If you participate in contact sports, wear a protective cup to shield the genital area from potential impacts and injuries.
Conclusion:
Penile cysts can be a bit bothersome, but they usually aren’t a big deal. Learning about the different types like epidermoid, sebaceous, inclusion, and median raphe cysts empowers you to take action if needed. Warm compresses and medical help are there when things get uncomfortable. Plus, your efforts to keep things clean, be mindful during intimacy, and protect yourself in sports play a role in prevention.
Don’t forget to visit the doctor if you notice something strange. They’ll help you figure things out and offer the best advice. Staying proactive and informed is the key to penile health and a worry-free future.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q. What are penile cysts, and why do they occur?
A: Penile cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on or beneath the skin of the penis. They’re often caused by blocked hair follicles or oil glands. Different types, like epidermoid and sebaceous cysts, form due to the accumulation of keratin or oil. Median raphe cysts, on the other hand, originate from developmental remnants along the raphe. These cysts are generally benign, but some may become infected or inflamed
Q. Are penile cysts contagious or a sign of a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
A. Penile cysts are not contagious and are typically unrelated to sexually transmitted infections. They often result from blocked hair follicles, oil glands, or developmental remnants.
Q. Can penile cysts cause complications or lead to other health issues?
A. While most penile cysts are benign and don’t pose significant health risks, there are potential complications. Cysts can become infected, inflamed, or painful, requiring medical attention. In rare cases, cysts might grow larger, impacting daily activities or causing cosmetic concerns.






































