Exploring the Effects of Masturbation on the Kidney

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr Dodda Basavaraj did his MBBS from Vijayanagara Institute Of Medical Sciences, Ballari . His domain of interest always lied in obstetrics , gynaecology and sexual health. He has worked as Medical officer, Tele-consultation doctor at tertiary and primary health care sectors in Karnataka . He believes strongly in medical practice which is evidence based, non-judgemental and patient centric.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 23 December, 2023
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.

"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
Masturbation is a natural and normal activity that is widely practiced by both men and women. It involves the act of self-stimulation to the point of orgasm. It is a common practice among people of all ages, and it has been known to have numerous health benefits. However, there is one interesting question, what are the masturbation effects on kidney?
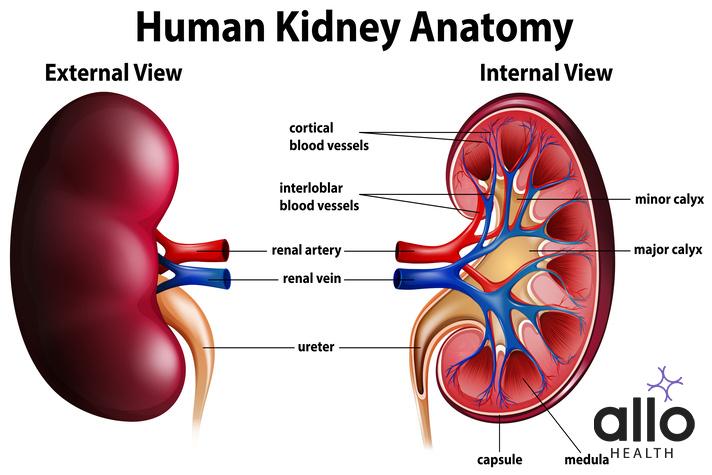
The Anatomy of the Kidney
The kidney is a vital organ responsible for maintaining the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body, filtering waste products from the blood, and producing urine. Understanding its anatomy is crucial to comprehending its function. Let’s delve into the anatomy of the kidney and explore its various components.
- Renal Capsule: The kidney is enveloped by a tough, fibrous layer called the renal capsule, which provides protection and maintains the organ’s shape.
- Renal Cortex: The outer region of the kidney is known as the renal cortex. It contains numerous nephrons, which are the functional units responsible for filtering the blood.
- Renal Medulla: Situated beneath the renal cortex, the renal medulla consists of renal pyramids. These pyramids contain tubules and ducts that transport urine towards the renal pelvis.
- Renal Pelvis: The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped structure located at the innermost region of the kidney. It collects urine from the renal pyramids and funnels it into the ureter, which carries urine to the urinary bladder.
- Nephrons: Nephrons are the microscopic units within the kidney that perform the primary functions of filtration and urine formation. Each kidney consists of approximately one million nephrons. A nephron comprises the following key components:
- Renal Corpuscle: The renal corpuscle consists of the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. The glomerulus is a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Blood entering the glomerulus is filtered under high pressure, separating waste products and excess substances from the blood. The filtered fluid then enters Bowman’s capsule.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): The filtered fluid from the glomerulus passes into the PCT, where reabsorption of essential substances such as water, glucose, amino acids, and ions occurs. This reabsorption helps maintain the body’s balance of fluids and electrolytes.
- Loop of Henle: The loop of Henle is a U-shaped structure divided into the descending limb and the ascending limb. It plays a vital role in reabsorbing water and electrolytes, concentrating the urine and establishing an osmotic gradient within the kidney.
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): The DCT is responsible for further reabsorption and secretion. It regulates the concentration of electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, as well as the pH balance of the blood.
- Collecting Ducts: The collecting ducts receive urine from multiple nephrons and carry it towards the renal pelvis. The final concentration of urine occurs here, influenced by hormonal signals like antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone.
- Renal Artery and Vein: The renal artery supplies oxygenated blood to the kidney, branching into smaller arterioles and eventually into the glomerular capillaries. After filtration, the blood leaves the kidney through the renal vein, which returns it to circulation.
- Renal Nerves: The kidneys receive nerve fibers from the sympathetic nervous system, which regulate renal blood flow, blood pressure, and the release of certain hormones.
What is Masturbation?
Masturbation is the act of self-stimulating the genitals to experience sexual pleasure and achieve sexual arousal. It is a normal and natural sexual activity that is commonly practiced by individuals of all genders and sexual orientations. Here is a comprehensive definition that delves into various aspects of masturbation:
- Self-Stimulation: Masturbation involves the deliberate and voluntary stimulation of one’s own genitals. This can be achieved through various techniques such as touching, rubbing, or massaging the genitals, including the clitoris, penis, labia, or anus.
- Sexual Pleasure and Arousal: The primary purpose of masturbation is to experience sexual pleasure and arousal. Engaging in this activity can result in physical and psychological sensations of pleasure, including muscle tension, increased heart rate, and release of endorphins.
- Solo Sexual Activity: Masturbation is typically performed individually, without the involvement of a partner. It allows individuals to explore their own bodies, desires, and preferences without external influences.
- Normal and Healthy Sexual Expression: Masturbation is considered a normal and healthy part of human sexuality. It is a private and personal form of sexual expression that does not involve any risks of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or unwanted pregnancies.
- Personal Exploration and Self-Discovery: Masturbation can serve as a means of self-exploration and self-discovery. It allows individuals to learn about their own bodies, sexual responses, and preferences, which can enhance their overall sexual experiences and intimate relationships.
- Stress Relief and Relaxation: Masturbation can provide stress relief and relaxation. It can help individuals alleviate tension, reduce anxiety, and promote a sense of well-being by releasing endorphins and inducing a state of relaxation.
- Sexual Release and Orgasm: Masturbation often culminates in sexual release and orgasm. Orgasm is the pleasurable climax of sexual stimulation, typically accompanied by intense physical and emotional sensations, as well as muscle contractions in the genital area.
- Varied Techniques and Tools: Masturbation techniques can vary widely among individuals, and people may use their hands, fingers, sex toys, or other objects to stimulate themselves. The choice of techniques and tools is a matter of personal preference and comfort.
- Privacy and Consent: Masturbation is a private and personal activity. It is essential to respect an individual’s privacy and refrain from engaging in non-consensual observation or intrusion into someone’s personal space while they are engaging in this activity.
Cultural and religious beliefs around masturbation can vary, and societal attitudes toward it can differ. Some individuals may experience feelings of guilt, shame, or confusion about masturbation due to these factors. However, it is essential to recognize that masturbation is a normal and natural aspect of human sexuality, and as long as it is done in a private and consensual manner, it is a personal choice that can contribute to a healthy and fulfilling sexual life.
The Connection between Masturbation and Kidney Health: Is there a Link?
There is no direct scientific evidence to suggest a link between masturbation and kidney health. Masturbation is a normal and natural sexual activity that does not have any detrimental effects on kidney function or overall kidney health. Here are some key points to consider:
- Kidney Function: The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood, regulating fluid and electrolyte balance, and producing urine. Their function is primarily related to the circulatory system and the filtration of blood, rather than sexual activities.
- Waste Elimination: The waste products eliminated by the kidneys are primarily metabolic waste and byproducts of bodily functions, such as urea and excess water, rather than substances related to sexual activity. These waste products are not influenced by or related to masturbation.
- Circulatory System: Masturbation is a form of sexual stimulation that primarily affects the sexual organs and the central nervous system. It does not directly impact the circulatory system or blood flow to the kidneys, which is crucial for their function.
- Urinary System: The urinary system, which includes the kidneys, bladder, and urethra, is responsible for eliminating urine from the body. Masturbation does not introduce any substances into the urinary system that would affect kidney health or function.
- General Health Considerations: While masturbation itself does not impact kidney health, certain lifestyle factors may indirectly affect both sexual activities and kidney function. These factors include overall health, cardiovascular health, and lifestyle habits such as maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. However, these considerations are not exclusive to masturbation but apply to overall well-being.
In the absence of underlying kidney conditions, masturbation is generally considered a safe and normal part of human sexuality, and there is no scientific evidence to suggest that it negatively impacts kidney health.
Myths About Masturbation and Kidney Health
- Myth 1: Masturbation causes kidney damage or disease.
Debunked: There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that masturbation causes kidney damage or disease. Kidney health is primarily influenced by factors such as genetics, overall health, hydration, and lifestyle habits, rather than sexual activities like masturbation. - Myth 2: Masturbation leads to kidney stones.
Debunked: Kidney stones are formed due to the accumulation of certain substances in the urine, such as calcium, oxalate, or uric acid. Masturbation does not introduce any additional substances into the urinary system that would contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Dietary factors, dehydration, and underlying medical conditions are more commonly associated with kidney stone formation. - Myth 3: Frequent masturbation depletes the body of essential nutrients.
Debunked: Masturbation does not cause any significant nutrient depletion in the body. While sexual activities, including masturbation, can lead to the release of hormones and neurotransmitters, the resulting changes in the body’s chemistry are temporary and do not result in nutrient deficiencies. - Myth 4: Masturbation weakens the kidneys.
Debunked: Masturbation does not weaken the kidneys or have any negative impact on kidney strength or function. Kidney health is influenced by factors such as genetics, overall health, and lifestyle habits, rather than sexual activities. - Myth 5: Masturbation increases the risk of kidney infections or urinary tract infections (UTIs). Debunked: Masturbation itself does not increase the risk of kidney infections or UTIs. These infections are typically caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing the hands before and after sexual activities, can help reduce the risk of infections.
- Myth 6: Masturbation causes kidney failure.
Debunked: There is no scientific evidence to suggest that masturbation causes kidney failure. Kidney failure is a complex medical condition typically caused by underlying health conditions, such as chronic kidney disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or certain medications. Sexual activities like masturbation are not a direct cause of kidney failure.
When To Seek Medical Help For Kidney Concerns
Detecting symptoms of kidney problems early on is crucial for prompt medical intervention and appropriate treatment. Here are common symptoms that may indicate kidney concerns and guidelines on when to seek medical help:
- Changes in Urination:
- Frequent urination or increased urge to urinate.
- Decreased urine output or difficulty in urinating.
- Blood in the urine (hematuria) or dark-colored urine.
- Foamy or bubbly urine.
- Swelling and Fluid Retention:
- Swelling (edema) in the legs, ankles, feet, or face.
- Puffiness around the eyes.
- Rapid weight gain due to fluid retention.
- Fatigue and Weakness:
- Persistent fatigue or feeling excessively tired.
- Generalized weakness or lack of energy.
- Difficulty concentrating or mental fogginess.
- Pain and Discomfort:
- Pain in the back, sides, or lower abdomen.
- Kidney pain can be dull, aching, or sharp.
- Kidney stones may cause severe pain in the flank area.
- Changes in Urine Appearance:
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
- Urgency or increased frequency of urination.
- Difficulty or pain during urination.
- High Blood Pressure:
- Hypertension that is difficult to control.
- Sudden increase in blood pressure.
- Development of high blood pressure at a young age.
- Nausea, Vomiting, and Loss of Appetite:
- Persistent nausea or vomiting.
- Loss of appetite or aversion to food.
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Skin Rash or Itching:
- Persistent itching, particularly in the legs.
- Dry, flaky skin or skin rashes.
- Pale skin or excessive bruising.
- Metallic Taste in the Mouth and Ammonia Breath:
- A persistent metallic taste in the mouth.
- Ammonia-like breath odor.
- Other Systemic Symptoms:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Swollen lymph nodes or enlarged tonsils.
- Joint pain or stiffness.
When to Seek Medical Help
- If you experience persistent or severe symptoms related to the kidneys.
- If you notice changes in urination patterns or urine appearance.
- If you have unexplained swelling or fluid retention.
- If you have persistent fatigue, weakness, or other systemic symptoms.
- If you have a history of kidney problems or have risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, or family history of kidney disease.
So, to summarize, There is no clear link between masturbation and kidney health. Masturbation is a healthy and natural activity that can have many positive effects on mental and physical health. While it is important to practice healthy masturbation habits, it is unlikely that masturbation will cause any long-term damage to the kidneys. By educating yourself on the myths and facts about masturbation and kidney health, and taking care of your overall well-being, you can maintain good kidney function and promote a healthy and satisfying sex life.
While masturbation itself does not have a direct impact on kidney health, certain underlying medical conditions can affect both kidney function and sexual health. For example, conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure can increase the risk of both kidney disease and erectile dysfunction. Therefore, it is important to manage any underlying health conditions and seek medical advice if you experience any changes in your sexual or urinary function.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Does masturbation have any negative effects on the kidneys?
A1: No, masturbation does not have any direct negative effects on the kidneys. The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and regulating fluid balance in the body. Masturbation is a normal and healthy sexual activity that does not pose any specific risk to kidney function.
Q2: Can excessive masturbation cause kidney damage?
A2: No, there is no scientific evidence to suggest that excessive masturbation can cause kidney damage. The kidneys are well-protected organs located in the back of the abdomen and are not directly affected by sexual activity. As long as masturbation is practiced in a safe and healthy manner, it does not pose a risk to kidney health.
Q3: Is there a link between masturbation and kidney stones?
A3: No, there is no direct link between masturbation and the formation of kidney stones. Kidney stones are usually caused by a combination of factors such as dehydration, diet, and genetics. Masturbation does not contribute to the development of kidney stones.
Q4: Can masturbation lead to urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney infections?
A4: Masturbation itself does not directly cause urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney infections. These infections are typically caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing the hands before masturbation, can help reduce the risk of infections. It is important to note that UTIs or kidney infections are not caused by the act of masturbation.
Q5: Should individuals with kidney problems avoid masturbation?
A5: In general, individuals with kidney problems can safely engage in masturbation. However, if you have a specific kidney condition or are undergoing treatment, it is advisable to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if any restrictions or precautions are necessary. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual health needs.






































