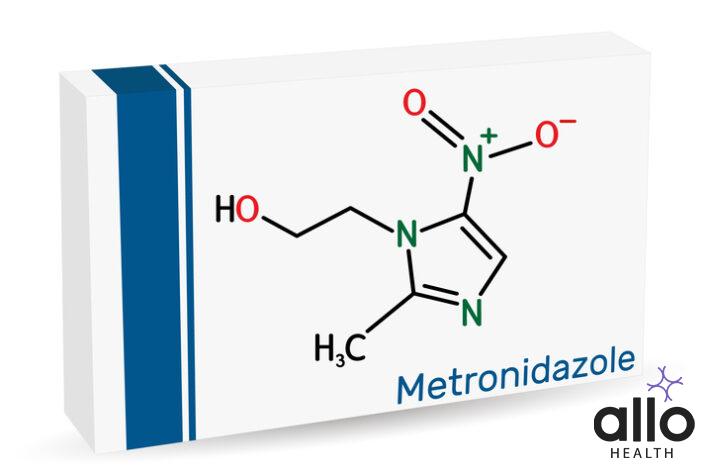
Metronidazole: A Comprehensive Guide to This Essential Antibiotic

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr Likhith earned a MBBS degree from Kharkiv National Medical University (Ukr, Eu) in 2019. He has hands-on experience in working within the healthcare domain & super specialty hospitals post completing his internship at St. Philomena's hospital, Bengaluru. His experience as a consultant physician in an Urban primary health centre led to his active involvement in various SORC camps under NUHM. He believes that sex education is one of the best investments society can make to promote sexual health with a positive attitude.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 26 December, 2023
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
"The following blog article provides information about a drug or brand name drug and its potential effects or benefits. However, it is crucial to understand that this information is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical consultation. It is highly recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions regarding medication, treatment, or healthcare management.
Book consultation
Individuals have unique medical conditions, and the information provided in this article may not be applicable to everyone. Only a qualified healthcare provider can evaluate your specific medical situation, taking into account your medical history, conducting appropriate tests, and providing personalized advice and recommendations. They are equipped to make informed decisions tailored to your individual needs.
It is crucial to emphasize that self-diagnosis, self-medication, or disregarding medical advice can have serious health consequences. This article may reference specific brand names or drugs for illustrative purposes. Mention of these names does not imply endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of their efficacy or safety. The choice of medication should be based on discussions and individualized guidance from a healthcare professional who has a comprehensive understanding of your medical condition.
"







































