Exploring the Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Ms Miriam is a licensed Clinical Psychologist and Psychotherapist, who completed her training and licencing from the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), and has experience in working with patients in areas of adult psychiatry, child and adolescent psychiatry, addiction medicine, neuropsychology and family & marital therapy.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 26 December, 2023
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
Are you struggling with anxiety, depression, addiction, or other mental health concerns? If so, you may be interested in exploring the benefits of CBT Therapy. It is a type of psychotherapy that has been shown to be effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions. In this article, we will explore the principles of CBT, the different types of CBT, the role of psychologists in CBT, and the benefits of CBT for a variety of mental health concerns.
What is CBT?
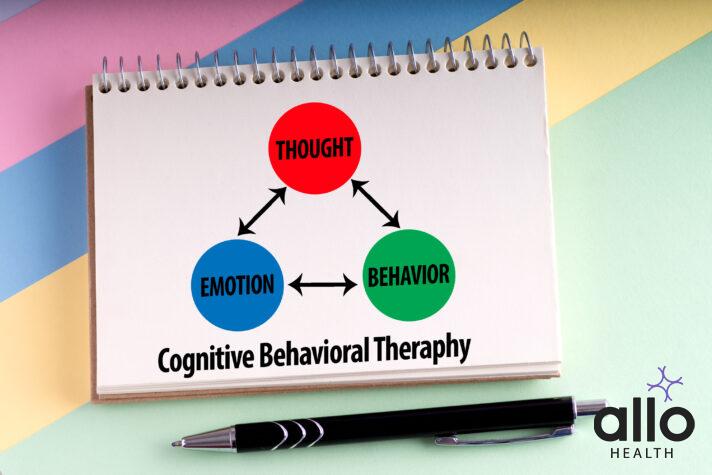
CBT is based on the principle that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected and that changing one can positively impact the others.
CBT is often used to treat a range of mental health conditions, including anxiety spectrum disorders, mood disorders, trauma related disorders, and sexual disorders, somatoform disorders, etc. It is a short-term, goal-oriented therapy that typically involves weekly sessions with a trained psychotherapist. During these sessions, the therapist works with the individual to identify negative thought patterns and behaviors and develop strategies to restructure these patterns.
The History of CBT
CBT was developed in the 1960s by Aaron Beck, a psychiatrist who was dissatisfied with the traditional psychoanalytic approach to therapy. He believed that depression and other mental health concerns were rooted in negative thought patterns and that by changing these patterns, individuals could experience lasting relief from their symptoms.
Beck’s initial work focused on depression, but he soon expanded his approach to include other mental health concerns, such as anxiety disorders and personality disorders. He also collaborated with other researchers and clinicians to refine and develop CBT techniques, such as exposure therapy for phobias and cognitive restructuring for negative thought patterns.
Today, CBT is one of the most widely used and researched forms of psychotherapy. It has been shown to be effective for a range of mental health concerns, including depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and eating disorders. CBT is often used in combination with medication and other forms of treatment, and it can be adapted to meet the unique needs of each individual client.
The Principles of CBT
The principles of CBT include identifying negative thought patterns, challenging these patterns, and replacing them with more balanced thoughts. CBT can also be accompanied by discussing with the client coping skills and behavioral strategies to manage symptoms and prevent relapse.
Another important principle of CBT is the emphasis on the present moment. CBT therapists encourage clients to focus on the here and now, rather than dwelling on past events or worrying about the future. This helps clients to develop a greater sense of control over their thoughts and emotions.
Additionally, CBT is often used in conjunction with other forms of therapy, such as medication or mindfulness practices. By combining different approaches, clients can receive a more comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and challenges.
How CBT Works
CBT typically involves weekly sessions with a therapist, and the duration of treatment can vary depending on the individual’s needs. In therapy, the therapist will work with the individual to identify negative thought patterns and behaviors and develop strategies for changing them. These strategies may involve practicing mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and cognitive restructuring.
Additionally, CBT may also involve homework assignments, such as maintaining a thought diary or practicing new coping skills outside of therapy sessions. The goal of CBT is to help individuals develop more positive and adaptive ways of thinking and behaving, which can lead to improved mental health and overall well-being.
Types Of Therapy: CBT
CBT is a widely used and effective form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. There are several different types of CBT, each with its own unique approach and techniques. Here are some of the most commonly practiced types of CBT:
- Traditional CBT: Traditional CBT, also known as Beckian CBT or simply CBT, was developed by Aaron T. Beck and is the foundation for many other variations. It emphasizes identifying and challenging negative or distorted thoughts and beliefs that contribute to emotional distress and maladaptive behaviors. Through this process, individuals learn to alter negative thinking patterns with more balanced thoughts, leading to improved emotional well-being and behavioral changes.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT was originally developed by Marsha M. Linehan to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD) but has since been adapted for other conditions. DBT combines standard CBT techniques with mindfulness practices, emphasizing acceptance and validation alongside change. It focuses on developing skills in four key areas: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): ACT is a form of CBT that aims to help individuals accept their thoughts and feelings rather than trying to eliminate or control them. It encourages individuals to identify their values and commit to taking actions aligned with those values, even in the presence of difficult thoughts and emotions. ACT emphasizes mindfulness, acceptance, cognitive diffusion, and values-driven behavioral change.
- Schema Therapy: Schema Therapy, developed by Jeffrey E. Young, integrates elements of cognitive-behavioral, psychodynamic, and experiential therapy. It focuses on identifying and modifying long-standing patterns of thinking and behavior called schemas, which develop during childhood and can influence current emotional difficulties and relationship patterns. Schema Therapy aims to help individuals understand and meet their unmet emotional needs while challenging and changing maladaptive schemas.
- Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT): CPT is specifically designed to treat individuals who have experienced trauma, particularly post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It combines cognitive therapy techniques with exposure therapy, helping individuals process traumatic events, challenge negative beliefs about the trauma, and develop more adaptive thoughts and behaviors. CPT often involves writing about the traumatic event and discussing related thoughts and emotions.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): MBCT integrates elements of CBT with mindfulness practices. It was initially developed to prevent relapse in individuals with recurrent depression but has been applied to various mental health conditions. MBCT combines meditation, body awareness, and cognitive strategies to help individuals become aware of their automatic thoughts, manage difficult emotions, and prevent relapse by interrupting negative thought patterns.
These are just a few examples of the different types of CBT available. Each approach has its own unique techniques and strategies, but all share the common goal of helping individuals identify and change unhelpful thoughts, emotions, and behaviors to improve their mental well-being. It’s important to note that the selection of a specific type of CBT depends on the individual’s needs and the expertise of the therapist.
Conditions That Can Be Treated with CBT
CBT is a versatile and evidence-based form of psychotherapy that can be effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions. Here are some of the conditions that can be treated with CBT:
- Depression: CBT is commonly used to treat depression. It helps individuals identify and challenge negative thinking patterns and beliefs that contribute to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and low self-esteem. By increasing awareness of errors in thinking and replacing negative thoughts with more balanced ones, CBT can improve mood and reduce depressive symptoms.
- Anxiety Disorders: CBT is highly effective in treating various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder (social phobia), specific phobias, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). CBT helps individuals identify and modify anxious thoughts and beliefs, develop coping strategies, and gradually face feared situations through exposure therapy.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): CBT, particularly Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) and Prolonged Exposure (PE), is widely used in the treatment of PTSD. CBT helps individuals process traumatic experiences, challenge and modify distorted thoughts and beliefs about the trauma, and develop effective coping strategies for managing trauma-related symptoms.
- Eating Disorders: CBT has been found to be effective in the treatment of eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder. It helps individuals identify and challenge distorted thoughts and beliefs related to body image, weight, and food, while also addressing unhealthy behaviors and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
- Substance Use Disorders: CBT is often used as part of substance abuse treatment programs. It helps individuals identify triggers and high-risk situations for substance use, develop strategies to cope with cravings and urges, and challenge and modify the underlying thoughts and beliefs that contribute to substance abuse.
- Insomnia: CBT for insomnia (CBT-I) is a specific form of CBT designed to treat chronic sleep concerns. It helps individuals identify and change thoughts and behaviors that contribute to sleep difficulties, establish a regular sleep routine, and develop relaxation techniques to improve sleep quality.
- Bipolar Disorder: CBT can be used as an adjunct treatment for individuals with bipolar disorder. It focuses on psychoeducation, mood monitoring, and identifying and challenging cognitive distortions associated with bipolar symptoms. CBT can also help individuals develop coping strategies to manage mood episodes and reduce the risk of relapse.
- Personality Disorders: CBT, particularly Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and Schema Therapy, has shown promise in treating various personality disorders. These approaches help individuals develop emotional regulation skills, improve interpersonal effectiveness, challenge maladaptive thoughts and behaviors, and address core beliefs underlying personality difficulties.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of CBT can vary from person to person, and the selection of treatment depends on the individual’s specific needs and the expertise of the therapist. CBT is often used in combination with other treatments, such as medication, and can be tailored to suit the unique circumstances of each individual.
The Role of Psychologists in Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
Psychologists play a crucial role in the delivery of CBT. They are trained professionals who have expertise in understanding and addressing mental health concerns using evidence-based techniques. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role a psychologist plays in CBT:
- Assessment and Diagnosis: Psychologists begin the CBT process by conducting a thorough assessment of the individual’s mental health. They use standardized assessment tools, interviews, and clinical judgment to gather information about the person’s symptoms, functioning, and relevant background history. This assessment helps psychologists make an accurate diagnosis and develop an individualized treatment plan.
- Collaborative Treatment Planning: Psychologists work collaboratively with the individual receiving therapy to develop a treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. They explain the principles of CBT, discuss the expected duration of treatment, and set achievable therapeutic targets. The treatment plan may include specific CBT techniques and strategies tailored to the individual’s condition.
- Psychoeducation: Psychologists provide psychoeducation to individuals undergoing CBT. They explain the nature of their condition, how thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected, and how CBT can help in addressing their concerns. Psychoeducation helps individuals gain a better understanding of their difficulties and empowers them to actively participate in the therapeutic process.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Psychologists guide individuals in identifying and challenging their negative or distorted thoughts and beliefs. They help individuals examine the evidence for and against these thoughts, consider alternative perspectives, and develop more balanced and realistic thinking patterns. Through this process, psychologists help individuals replace unhelpful thoughts with more adaptive ones, leading to emotional and behavioral changes.
- Behavioral Experiments: Psychologists design and implement behavioral experiments as part of CBT. These experiments involve testing out new behaviors or ways of thinking to gather evidence and challenge existing beliefs. Psychologists guide individuals in planning and carrying out these experiments, helping them evaluate the outcomes and adjust their beliefs and behaviors accordingly.
- Exposure Therapy: In cases of anxiety disorders and PTSD, psychologists use exposure therapy, a key component of Behavioral Therapy. They systematically expose individuals to feared situations or traumatic memories in a safe and controlled manner, helping them gradually confront and reduce their anxiety or distress, and then use aspects of CBT to work through thought patterns.
- Skill-Building: Psychologists teach individuals specific skills and techniques to manage their symptoms and improve their functioning. This may include stress management techniques, relaxation exercises, problem-solving skills, emotion regulation strategies, and social skills training. Psychologists provide guidance, feedback, and support as individuals learn and practice these skills both during therapy sessions and in their daily lives.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Psychologists regularly monitor and evaluate the progress of individuals undergoing CBT. They assess treatment outcomes, track changes in symptoms, and monitor the effectiveness of CBT techniques. Psychologists use this information to make adjustments to the treatment plan, provide feedback to individuals, and ensure that therapy is aligned with the person’s evolving needs.
- Relapse Prevention: As therapy progresses and individuals experience improvements, psychologists focus on relapse prevention. They help individuals identify potential triggers, develop coping strategies to manage setbacks, and reinforce the skills and techniques learned during therapy. Psychologists work with individuals to create a plan for maintaining progress and managing future challenges independently.
Throughout the therapy process, psychologists maintain a supportive and non-judgmental stance. They establish a therapeutic alliance, foster a safe and trusting environment, and provide empathy and validation to individuals. Psychologists also adhere to ethical guidelines and maintain professional boundaries to ensure the highest standard of care.
Find a CBT Therapist
If you’re interested in exploring CBT therapy, the first step is to find a qualified therapist near you. You can ask for a referral from your primary care physician, contact your health insurance provider, or search online databases of licensed psychologists in your area.
Another option is to ask for recommendations from friends or family members who have undergone CBT therapy. They may be able to provide valuable insights into their experience and recommend a therapist who they found helpful.
It’s important to do your research and find a therapist who is experienced in CBT and has a good reputation. You can read online reviews or check with professional organizations such as the Association for Behavioral and Cognitive therapists to find a qualified therapist in your area.
What to Expect During Your First CBT Session
If you’re looking to find a CBT therapist in India, here’s a detailed guide on how to go about it:
- Research and Understand CBT: Before seeking a therapist, it’s helpful to have a basic understanding of CBT. Learn about its principles, techniques, and the specific mental health conditions it can address. This knowledge will enable you to make informed decisions and engage in meaningful discussions with potential therapists.
- Seek Referrals: Start by asking for referrals from trusted sources, such as your primary care physician, friends, family, or other healthcare professionals. They may have recommendations for CBT therapists they trust or have had positive experiences with. Online communities and support groups related to mental health can also be valuable resources for recommendations.
- Online Directories and Professional Associations: Several online directories and professional associations provide lists of therapists. Websites like Psychology Today, Practo, and GoodTherapy allow you to search for CBT therapists based on location, specialization, and other criteria. Additionally, professional associations like the Indian Association of Clinical Psychologists (IACP) or the Indian Psychiatric Society (IPS) may have directories or referral services to help you find qualified therapists.
- Contact Mental Health Institutions: Reach out to mental health institutions, clinics, or hospitals in your area. Inquire about their services and whether they have CBT therapists on staff or can provide recommendations. These institutions often have a network of mental health professionals and can guide you to appropriate resources.
- Check Therapists’ Credentials: Once you have a list of potential CBT therapists, check their credentials and qualifications. Look for psychologists or therapists who have specific training and experience in CBT. Check if they are licensed or registered with professional bodies like the Rehabilitation Council of India (RCI) or the respective states psychological associations.
- Assess Experience and Specializations: Review the therapists’ profiles, websites, or professional listings to learn about their experience and areas of specialization. Look for therapists who have expertise in treating the specific condition you seek help for. CBT therapists may specialize in areas such as anxiety disorders, depression, trauma, eating disorders, or substance abuse.
- Consider Logistics: Take into account practical considerations such as location, availability, and affordability. Ensure that the therapist’s clinic or practice is accessible to you and aligns with your schedule. Inquire about session fees, insurance coverage, and any available sliding scale options for reduced fees if needed.
- Initial Consultation: Contact the therapists on your shortlist and schedule an initial consultation. This may be an in-person meeting, a phone call, or a video consultation. Use this opportunity to ask questions about their approach, experience, and how they structure CBT sessions. Assess their communication style, rapport, and whether you feel comfortable working with them.
- Verify Confidentiality and Ethics: Discuss confidentiality and the therapist’s approach to ethical considerations during the initial consultation. Ensure they adhere to professional guidelines and maintain the privacy and confidentiality of your sessions.
- Trust Your Instincts: Ultimately, trust your instincts and choose a therapist with whom you feel a connection and sense of trust. Feeling comfortable and understood is essential for the therapeutic process to be effective.
The Benefits of CBT Treatment
Depression
CBT is widely recognized as an effective treatment for depression. Here are the detailed benefits of CBT for depression:
- Addressing Negative Thought Patterns: CBT focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to depression. It helps individuals recognize cognitive distortions that they may be relying on and employing too much and helps them in identifying and replacing negative thoughts with more realistic and balanced ones, CBT can improve mood and reduce depressive symptoms.
- Developing Coping Strategies: CBT equips individuals with practical coping strategies to manage depressive symptoms. It helps individuals develop skills to deal with stress, solve problems, and regulate emotions. By learning effective coping mechanisms, individuals can better handle the challenges and triggers that contribute to their depression.
- Behavioral Activation: CBT includes behavioral activation techniques that encourage individuals to engage in activities they once enjoyed but may have lost interest in due to the disorder. By gradually reintroducing pleasurable activities and increasing engagement in rewarding experiences, CBT helps restore a sense of pleasure, motivation, and fulfillment in life.
- Increasing Awareness of Triggers: CBT helps individuals identify specific triggers or situations that worsen their depressive symptoms. Through therapy, individuals become more aware of these triggers and learn strategies to deal with them. This increased awareness empowers individuals to proactively address and minimize the impact of triggering factors.
- Problem-Solving Skills: teaches individuals problem-solving skills to effectively address difficulties and stressors contributing to their depression. It involves breaking down concerns into manageable steps, generating and evaluating potential solutions, and implementing and evaluating the outcomes. By developing problem-solving skills, individuals feel more empowered and confident in managing life challenges.
- Managing Rumination: CBT addresses rumination, which is a common symptom of depression characterized by repetitive and negative patterns of thinking. Therapists help individuals recognize rumination patterns and develop strategies to interrupt and redirect these thoughts. By reducing rumination, individuals can break free from negative thought cycles and experience improved mood and well-being.
- Relapse Prevention: CBT focuses on equipping individuals with skills to prevent relapse and maintain long-term recovery from depression. Therapists work with individuals to develop relapse prevention plans, identify early warning signs of relapse, and implement strategies to manage and minimize the risk of recurrence. This helps individuals build resilience and maintain their progress beyond the course of therapy.
- Enhanced Self-Esteem and Self-Compassion: CBT promotes self-awareness and helps individuals challenge self-critical and self-defeating thoughts. Through therapy, individuals learn to develop a more compassionate and accepting attitude towards themselves. This shift in self-perception can improve self-esteem and foster a more positive self-image.
- Increased Problem-Solving Orientation: CBT encourages individuals to take an active and problem-solving approach to their depression. It helps individuals develop a sense of agency and responsibility in addressing their symptoms. This proactive stance empowers individuals to take control of their mental health and make positive changes in their lives.
- Effectiveness and Long-Term Benefits: Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of CBT in treating depression. Research shows that CBT can lead to significant and long-lasting reductions in depressive symptoms. It is often recommended as a first-line treatment for depression due to its evidence-based nature and ability to equip individuals with lifelong skills for managing depressive symptoms.
Anxiety Disorders
CBT is highly effective in treating anxiety disorders. It focuses on identifying and addressing the underlying thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. Here are the detailed benefits of CBT for anxiety disorders:
- Identifying and Challenging Negative Thought Patterns: CBT helps individuals recognize and challenge negative thought patterns and irrational beliefs that contribute to anxiety. It assists in identifying automatic negative thoughts and replacing them with more rational and realistic ones. By altering thought patterns, individuals can reduce anxiety and gain a more balanced perspective.
- Understanding the Connection between Thoughts, Emotions, and Behaviors: CBT helps individuals understand the interplay between their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors in anxiety-provoking situations. By recognizing how thoughts and behaviors influence emotions, individuals can identify and modify unhelpful responses. This understanding empowers individuals to respond to anxiety-provoking situations in a more adaptive and constructive manner.
- Gradual Exposure and Desensitization: CBT incorporates exposure techniques to gradually and safely confront feared situations or stimuli. Therapists guide individuals through exposure exercises to help them confront their fears and anxieties in a systematic and controlled manner. Over time, this exposure desensitizes individuals to the anxiety-inducing stimuli, leading to reduced anxiety responses.
- Relaxation and Stress Management: CBT teaches individuals relaxation techniques and stress management strategies to reduce anxiety. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness techniques are commonly employed in CBT. These techniques help individuals relax their bodies, calm their minds, and cope with stressors, ultimately reducing anxiety symptoms.
- Behavioral Experiments: CBT involves conducting behavioral experiments to test the accuracy of anxious thoughts and beliefs. Individuals engage in real-life experiences that challenge their anxious predictions. By collecting evidence through these experiments, individuals can reevaluate their anxious thoughts and develop more realistic and accurate beliefs, leading to a reduction in anxiety.
- Cognitive Restructuring: CBT assists individuals in identifying and restructuring maladaptive thought patterns associated with anxiety. Through cognitive restructuring, individuals learn to identify and challenge distorted or unhelpful thoughts that contribute to anxiety. They replace these thoughts with more rational and balanced alternatives, reducing anxiety and promoting a more positive mindset.
- Problem-Solving Skills: CBT equips individuals with problem-solving skills to address the challenges and stressors that contribute to anxiety. Individuals learn how to break down problems into manageable steps, generate and evaluate potential solutions, and implement effective strategies. By developing problem-solving skills, individuals gain a sense of control over their anxiety and feel more confident in managing difficult situations.
- Education about Anxiety: CBT provides individuals with education about anxiety, its causes, and its symptoms. Understanding the nature of anxiety and its underlying mechanisms helps individuals gain insights into their experiences. Psychoeducation also helps normalize anxiety symptoms, reducing self-judgment and fostering self-compassion.
- Relapse Prevention: CBT focuses on relapse prevention by equipping individuals with skills and strategies to maintain their progress and prevent the recurrence of anxiety symptoms. Therapists work with individuals to identify triggers, develop coping mechanisms, and create personalized relapse prevention plans. This proactive approach helps individuals sustain long-term improvements in managing anxiety.
- Empowerment and Self-Efficacy: CBT empowers individuals to take an active role in managing their anxiety. By learning and applying CBT techniques, individuals gain a sense of self-efficacy and confidence in their ability to cope with anxiety. This empowerment allows individuals to take control of their anxiety symptoms and live a more fulfilling life.
Treating Eating Disorders
CBT has been found to be highly effective in the treatment of eating disorders. It addresses the underlying thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors associated with disordered eating patterns. Here are the detailed benefits of CBT for treating eating disorders:
- Identifying and Challenging Distorted Thoughts and Beliefs: CBT helps individuals with eating disorders identify and challenge distorted thoughts and beliefs related to body image, food, and weight. It focuses on addressing negative self-perceptions, unrealistic standards, and irrational beliefs that contribute to disordered eating behaviors. By challenging and replacing these distorted thoughts, individuals can develop a healthier relationship with food and body image.
- Behavioral Monitoring and Meal Planning: CBT involves monitoring and tracking eating behaviors, thoughts, and emotions associated with food intake. It helps individuals establish regular and balanced eating patterns, which are essential for recovery. Meal planning and structured eating routines are incorporated to establish a sense of control and normalize eating habits.
- Coping Skills Development: CBT equips individuals with coping skills to manage triggers, emotional distress, and anxiety related to food and body image. It focuses on teaching alternative coping strategies to replace maladaptive behaviors such as binge eating, purging, or restrictive eating. Individuals learn healthier ways to manage stress, regulate emotions, and cope with body dissatisfaction.
- Body Image Distortion and Acceptance: CBT addresses body image distortion, helping individuals develop a more realistic and positive perception of their bodies. Therapists work with individuals to challenge unrealistic societal standards and promote body acceptance. By fostering a healthier body image, individuals can reduce body-related anxiety and improve their overall well-being.
- Cognitive Restructuring: CBT assists individuals in identifying and restructuring negative and self-critical thoughts related to their body, weight, and eating behaviors. Individuals learn to challenge and replace these thoughts with more balanced and accurate ones. By changing their thought patterns, individuals can develop healthier attitudes towards food, weight, and body image.
- Emotion Regulation: CBT helps individuals develop effective emotion regulation strategies to address emotional triggers associated with eating disorders. Individuals learn to identify and manage emotions in healthier ways, reducing the need to rely on disordered eating behaviors as a means of emotional regulation. By enhancing emotion regulation skills, individuals can cope with emotions without resorting to unhealthy eating patterns.
- Relapse Prevention: CBT focuses on relapse prevention by equipping individuals with tools and strategies to maintain their recovery from eating disorders. Therapists help individuals identify warning signs, develop coping skills, and create personalized relapse prevention plans. This comprehensive approach supports individuals in sustaining long-term recovery and preventing relapses.
- Interpersonal Skills and Support: CBT addresses social and interpersonal factors that contribute to eating disorders. Therapists work with individuals to improve communication skills, assertiveness, and boundary-setting in relationships. Building a support network and involving loved ones in the treatment process can enhance the effectiveness of CBT for eating disorders.
- Self-Esteem and Self-Identity: CBT focuses on improving self-esteem and fostering a positive self-identity that is not solely based on body shape or weight. Therapists help individuals develop a more balanced and compassionate view of themselves, independent of their appearance. By cultivating self-worth and self-acceptance, individuals can reduce reliance on disordered eating behaviors as a means of self-validation.
- Long-Term Behavior Change: CBT aims to create lasting behavior change by helping individuals develop sustainable and healthy eating patterns. It emphasizes the importance of gradual and realistic goals, as well as the adoption of lifestyle changes that promote overall well-being. By focusing on long-term behavior change, CBT supports individuals in maintaining a healthy relationship with food and body image.
Treat Substance Abuse and Addiction
CBT is an evidence-based treatment approach that has shown significant benefits in addressing substance abuse and addiction. Here are the detailed benefits of CBT for treating substance abuse and addiction:
- Identifying and Challenging Unhelpful Thoughts and Beliefs: CBT helps individuals with substance abuse and addiction identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts and beliefs related to drug or alcohol use. It focuses on addressing distorted thinking patterns and rationalizations that contribute to addictive behaviors. By challenging these thoughts, individuals can develop more realistic and healthier beliefs about substance use.
- Building Coping Skills: CBT equips individuals with coping skills to manage triggers, cravings, and high-risk situations associated with substance abuse. Individuals learn techniques to identify and cope with stress, manage cravings, and handle difficult emotions without resorting to substance use. By developing alternative coping strategies, individuals enhance their ability to navigate challenging situations without relying on substances.
- Relapse Prevention: CBT places significant emphasis on relapse prevention. Therapists work with individuals to identify personal triggers, early warning signs of relapse, and develop strategies to manage them effectively. Through CBT, individuals gain the skills and tools to prevent relapse and maintain long-term recovery.
- Motivation Enhancement: CBT helps individuals increase motivation to change their addictive behaviors. Therapists explore the reasons behind substance use, help individuals identify personal goals, and facilitate the development of intrinsic motivation to overcome addiction. By enhancing motivation, individuals are more likely to actively engage in the treatment process and make positive changes.
- Behavior Modification: CBT focuses on behavior modification techniques to address addictive behaviors. Therapists work with individuals to identify and modify behaviors that contribute to substance abuse, such as avoiding high-risk situations, developing healthier routines, and establishing new habits. By replacing maladaptive behaviors with healthier alternatives, individuals can break the cycle of addiction.
- Cognitive Restructuring: CBT helps individuals recognize and challenge cognitive distortions and automatic thoughts associated with substance abuse. Therapists assist individuals in reframing irrational beliefs and developing more balanced and rational thinking patterns. By restructuring cognitive processes, individuals can change their attitudes towards substances and reduce the desire to use them.
- Developing Problem-Solving Skills: CBT focuses on helping individuals develop effective problem-solving skills to manage challenges and stressors that may lead to substance use. Individuals learn how to identify and evaluate potential solutions, make informed decisions, and implement strategies to address problems without resorting to substances. These skills empower individuals to handle life difficulties in a healthy and constructive manner.
- Enhancing Coping with Co-Occurring Mental Health Concerns: CBT can address co-occurring mental health conditions that often accompany substance abuse and addiction, such as anxiety or depression. By addressing both the substance use and the underlying mental health concerns, CBT provides a comprehensive approach to treatment, improving overall well-being and reducing the risk of relapse.
- Building Supportive Networks: CBT helps individuals build a supportive network of family, friends, or support groups to aid in their recovery. Therapists assist individuals in identifying healthy relationships and improving communication and interpersonal skills. By fostering a supportive environment, individuals can rely on social connections for encouragement, accountability, and assistance in maintaining sobriety.
- Empowering Self-Management: CBT empowers individuals to take an active role in their recovery process. By learning and applying CBT techniques, individuals develop self-management skills, self-monitoring abilities, and a sense of personal responsibility. This active engagement fosters self-efficacy and empowers individuals to make positive choices and maintain long-term recovery.
Group CBT Sessions
CBT can be conducted in both individual and group therapy settings. Group CBT therapy sessions offer several unique benefits that contribute to the effectiveness of treatment. Here are the detailed benefits of group CBT therapy sessions:
- Shared Support and Validation: Group CBT therapy provides individuals with a sense of belonging and understanding. Being in a group setting allows participants to connect with others who are going through similar experiences. Sharing stories, struggles, and successes with group members can provide a sense of validation, reducing feelings of isolation and fostering a supportive environment.
- Learning from Others: Group therapy offers the opportunity to learn from the experiences and insights of other group members. Participants can gain different perspectives on their challenges and learn from the coping strategies and techniques that have worked for others. Observing the progress and successes of fellow group members can provide hope and inspiration for one’s own journey.
- Developing Social Skills: Group CBT therapy sessions provide a platform for individuals to improve their social skills and enhance their ability to interact effectively with others. Group members can practice active listening, expressing themselves assertively, giving and receiving feedback, and providing support to others. These skills are transferable to various social contexts and can contribute to improved interpersonal relationships.
- Increased Accountability and Motivation: Being part of a group creates a sense of accountability as individuals share their goals and progress with others. The supportive atmosphere and encouragement from fellow group members can enhance motivation to actively participate in therapy and make positive changes. The shared commitment to personal growth and recovery can help individuals stay focused and dedicated to their treatment goals.
- Enhanced Empathy and Perspective-Taking: Group CBT therapy sessions foster empathy and perspective-taking skills. By listening to and empathizing with the experiences of others, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of different perspectives and challenges related to their own concerns. This enhanced empathy can promote personal growth, compassion, and a broader perspective on one’s own struggles.
- Peer Feedback and Support: Group therapy provides a unique opportunity for receiving feedback and support from peers who have similar experiences. Group members can offer insights, suggestions, and alternative perspectives in a non-judgmental and safe environment. This feedback can help individuals gain new insights, challenge unhelpful thinking patterns, and develop effective coping strategies.
- Social Learning and Modeling: Group CBT therapy sessions allow individuals to witness the progress and successes of others. Observing the growth and positive changes in fellow group members can serve as inspiration and provide evidence that recovery is possible. Witnessing others overcome challenges and develop new coping skills can instill hope and motivation in individuals for their own recovery.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Group CBT therapy sessions can be more cost-effective compared to individual therapy. The shared session time and resources among group members make therapy more affordable and accessible for individuals who may have financial limitations. This makes group therapy a valuable option for those seeking CBT treatment.
- Normalizing Experiences: Group CBT therapy sessions help individuals realize that they are not alone in their struggles. Hearing others share similar experiences and challenges can normalize their own experiences and reduce feelings of shame or self-blame. Understanding that others face similar difficulties can increase self-acceptance and decrease the sense of isolation.
- Continuity of Support: Group CBT therapy can provide a sense of continuity and ongoing support. Participants can develop long-lasting connections and friendships with fellow group members, creating a network of support beyond the therapy sessions. This ongoing support can contribute to maintaining progress, preventing relapse, and promoting sustained well-being.
Group CBT therapy sessions can be particularly beneficial for individuals who thrive in a social setting, enjoy collaborative learning, and benefit from the support and shared experiences of others. However, the suitability of group therapy may vary depending on individual preferences and the specific nature
How to Incorporate CBT Techniques into Your Daily Life
Incorporating CBT techniques into your daily life can be a powerful way to promote positive changes in your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Here are some detailed steps on how to incorporate CBT techniques into your daily routine:
- Identify Specific Goals: Start by identifying specific areas or goals you would like to work on using CBT techniques. It could be managing stress, challenging negative thoughts, improving communication skills, or developing healthier habits. Having clear goals will help you focus your efforts and measure your progress.
- Increase Self-Awareness: Pay attention to your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors throughout the day. Practice mindfulness and self-reflection to become aware of any negative or unhelpful patterns that may be contributing to your difficulties. Notice the connection between your thoughts, emotions, and actions.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: When you catch yourself engaging in negative or self-defeating thoughts, challenge them using CBT techniques such as cognitive restructuring. Identify the evidence supporting or refuting these thoughts and consider alternative, more realistic interpretations. Replace negative thoughts with positive and balanced ones.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation, into your daily routine. These techniques can help reduce stress, promote calmness, and improve overall well-being. Dedicate a few minutes each day to practice these techniques, especially during times of heightened stress or anxiety.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your larger goals into smaller, manageable steps. Set realistic and achievable goals for yourself, both short-term and long-term. This will help you stay motivated and maintain a sense of accomplishment as you make progress towards your larger goals.
- Journaling: Keep a journal to track your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Write down any negative thoughts or beliefs that arise, and challenge them using CBT techniques. Reflect on your experiences, noting any patterns or triggers. Journaling can help increase self-awareness, facilitate cognitive restructuring, and track your progress over time.
- Practice Behavioral Activation: Engage in activities that bring you joy, fulfillment, or a sense of achievement. Engaging in pleasurable and meaningful activities can improve your mood and overall well-being. Make a list of activities you enjoy and schedule time for them regularly.
- Use Thought Records: Utilize thought records to examine the connection between your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. When you notice a negative emotion or behavior, write down the triggering event, your thoughts, the resulting emotions, and the behaviors that follow. Challenge any irrational thoughts or cognitive distortions using evidence-based reasoning.
- Seek Social Support: Share your goals and progress with trusted friends, family, or support groups. Engage in discussions about CBT techniques and strategies with others who may be interested. Having social support can provide encouragement, accountability, and additional perspectives on your journey.
- Practice Regular Self-Care: Prioritize self-care activities such as getting enough sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, and practicing relaxation techniques. Taking care of your physical and emotional well-being provides a solid foundation for incorporating CBT techniques into your daily life.
Remember that incorporating CBT techniques into your daily life requires consistent practice and effort. Start with small steps and gradually increase your use of these techniques. Over time, they will become more natural and integrated into your daily routine, leading to positive changes in your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Alternatives to CBT
CBT is just one type of psychotherapy among many that are available. Here, we will compare CBT with a few other popular types of psychotherapy in detail:
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Psychodynamic therapy focuses on exploring how past experiences, especially in early childhood, shape a person’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. It emphasizes the unconscious processes and unresolved conflicts that may influence current difficulties. Psychodynamic therapy involves building a strong therapeutic relationship and encourages self-reflection, insight, and understanding. It aims to uncover unconscious patterns and promote healing through exploration of deep-rooted concerns. Unlike CBT, psychodynamic therapy may be less structured and more open-ended, with the therapist taking an active interpretive role.
- Humanistic Therapy: Humanistic therapy, also known as person-centered therapy, places emphasis on self-actualization, personal growth, and self-awareness. It views individuals as having the capacity for self-healing and focuses on the present moment and individual’s subjective experiences. Humanistic therapy emphasizes empathy, unconditional positive regard, and active listening from the therapist to foster a safe and supportive therapeutic environment. The therapist’s role is to facilitate self-exploration, self-acceptance, and personal empowerment. Unlike CBT, humanistic therapy may be less directive and does not typically employ structured techniques or homework assignments.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): ACT combines mindfulness-based techniques with strategies to accept and embrace difficult thoughts and feelings, while committing to actions aligned with personal values. It emphasizes psychological flexibility and the ability to be present in the moment. ACT encourages individuals to let go of attempts to control or avoid distressing experiences and instead focuses on accepting and living in accordance with personal values. It incorporates mindfulness exercises, cognitive defusion techniques, and values clarification exercises. Unlike CBT, ACT places less emphasis on challenging or changing negative thoughts and more on acceptance and values-driven actions.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT was initially developed to treat borderline personality disorder, but it has proven effective for various conditions characterized by emotional dysregulation. DBT combines elements of CBT with mindfulness techniques and incorporates both individual therapy and group skills training. It focuses on developing skills in emotion regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness. DBT provides a structured and comprehensive approach to help individuals cope with intense emotions, self-destructive behaviors, and difficulties in relationships. Unlike CBT, DBT places a particular emphasis on validation and accepting the person as they are, while also encouraging change.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Psychodynamic therapy focuses on exploring how past experiences, especially in early childhood, shape a person’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. It emphasizes the unconscious processes and unresolved conflicts that may influence current difficulties. Psychodynamic therapy involves building a strong therapeutic relationship and encourages self-reflection, insight, and understanding. It aims to uncover unconscious patterns and promote healing through exploration of deep-rooted concerns. Unlike CBT, psychodynamic therapy may be less structured and more open-ended, with the therapist taking an active interpretive role.
It’s important to note that the choice of psychotherapy depends on various factors, including the individual’s specific needs, preferences, and the nature of the presenting problem. Different therapeutic approaches may be more effective for different individuals and conditions. Additionally, therapists may integrate techniques from different approaches or use an eclectic approach that combines elements of multiple therapy to suit the individual’s needs. It’s recommended to consult with a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate type of therapy for your specific situation.
The Future of CBT: Advancements and Innovations
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has a strong evidence base and has been widely used to treat a range of mental health conditions. As the field of psychotherapy continues to evolve, several advancements and innovations are shaping the future of CBT. Here are some of the key developments:
- Technology-Assisted CBT: Advancements in technology have led to the development of technology-assisted CBT interventions. This includes computer-based programs, mobile applications, and online platforms that deliver CBT techniques and interventions. These tools can provide greater accessibility, convenience, and cost-effectiveness, making CBT more widely available to individuals who may not have access to traditional therapy. Technology-assisted CBT also allows for ongoing monitoring, feedback, and self-help resources.
- Virtual Reality (VR) CBT: Virtual reality is emerging as a promising tool in CBT. VR can create immersive environments that simulate real-life situations and triggers, providing a safe and controlled space for individuals to confront and work through their fears or anxieties. VR can be used in exposure therapy for phobias, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and other anxiety disorders. It offers a realistic and interactive experience that enhances engagement and effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
- Transdiagnostic Approaches: Traditional CBT approaches have been developed for specific disorders. However, transdiagnostic approaches are gaining recognition and popularity. These approaches focus on underlying commonalities and processes across different disorders, targeting core cognitive and behavioral mechanisms that contribute to psychopathology. Transdiagnostic CBT allows for more efficient and flexible treatment by addressing multiple disorders or symptoms simultaneously, rather than treating each disorder separately.
- Personalized and Tailored Interventions: The future of CBT involves greater personalization and tailoring of interventions to meet individual needs. Advances in technology, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, can help identify individual patterns, predict treatment response, and guide treatment planning. Personalized CBT interventions take into account specific characteristics, preferences, and goals of the individual, leading to more targeted and effective treatment.
- Integration of Neuroscience: As our understanding of the brain and its mechanisms improves, there is increasing integration of neuroscience into CBT. Neuroscientific research can provide insights into the neural processes underlying psychological disorders and inform the development of targeted interventions. Techniques such as neurofeedback, which allows individuals to monitor and regulate their own brain activity, are being explored as potential adjuncts to CBT.
- Cultural Adaptations: Recognizing the importance of cultural factors in therapy, there is a growing emphasis on culturally adapted CBT interventions. Culturally adapted CBT takes into account the cultural beliefs, values, and practices of diverse populations. It acknowledges the influence of cultural factors on the experience and expression of mental health symptoms and tailors interventions accordingly. Culturally adapted CBT aims to improve engagement, acceptability, and effectiveness of therapy among diverse populations.
- Integration of CBT with Other Modalities: CBT is increasingly being integrated with other therapeutic modalities to enhance treatment outcomes. For example, combining CBT with mindfulness-based techniques, such as mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), can enhance emotional regulation and relapse prevention. Integration of CBT with complementary therapy, such as yoga or art therapy, can provide additional avenues for self-expression and healing.
- Advancements in Training and Delivery: Efforts are being made to enhance the training and delivery of CBT. Training programs are incorporating the latest evidence-based practices, innovations, and technology to prepare therapists for the future. Additionally, efforts are underway to increase the dissemination and implementation of CBT in various settings, including primary care, schools, and community mental health centers, to make CBT more accessible to diverse populations.
CBT For Sexual Dysfunctions
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can be beneficial in treating sexual dysfunctions by addressing the psychological factors that contribute to the difficulties experienced. Here are some specific benefits of CBT for sexual dysfunctions:
- Addressing Psychological Factors: Sexual dysfunctions often have psychological components, such as performance anxiety, negative beliefs about sex, relationship concerns, or past traumas. CBT helps identify and address these underlying psychological factors that may be contributing to the sexual difficulties. By challenging and modifying negative or unhelpful thoughts and beliefs, individuals can develop a healthier mindset and reduce anxiety or distress related to their sexual experiences.
- Changing Maladaptive Sexual Behaviors: CBT aims to modify maladaptive behaviors that may contribute to sexual dysfunctions. Through behavioral techniques, individuals can learn new skills and strategies to enhance sexual functioning. For example, techniques like sensate focus exercises can help couples increase intimacy and reduce performance pressure. By replacing unhelpful or problematic behaviors with healthier alternatives, CBT can improve sexual functioning and satisfaction.
- Enhancing Communication and Relationship Skills: Sexual dysfunctions can significantly impact relationships and communication between partners. CBT focuses on improving communication skills, increasing understanding, and fostering emotional connection within the relationship. By addressing relationship concerns and promoting healthy communication patterns, CBT can enhance overall sexual satisfaction and intimacy.
- Managing Performance Anxiety: Performance anxiety is a common psychological factor associated with sexual dysfunctions. CBT provides individuals with tools to manage anxiety, such as relaxation techniques, cognitive restructuring, and exposure-based exercises. By reducing anxiety and performance pressure, individuals can experience greater comfort and enjoyment during sexual encounters.
- Developing Sensate Focus and Mindfulness: CBT often incorporates sensate focus exercises and mindfulness techniques to promote present-moment awareness, relaxation, and body acceptance. Sensate focus exercises involve non-sexual touch and focus on experiencing pleasure without the pressure of performance. Mindfulness techniques can help individuals cultivate a non-judgmental and accepting attitude towards their sexual experiences, reducing self-critical thoughts and increasing overall satisfaction.
- Managing Trauma-Related concerns: Individuals with sexual dysfunctions related to past traumatic experiences can benefit from CBT’s trauma-focused approaches. Therapists trained in trauma-focused CBT can help individuals process and heal from past traumas, reduce trauma-related symptoms, and address their impact on sexual functioning. This can involve techniques such as cognitive restructuring, exposure therapy, and grounding exercises.
- Maintenance and Relapse Prevention: CBT equips individuals with skills and strategies to maintain progress and prevent relapse. By identifying potential triggers, developing coping mechanisms, and fostering resilience, individuals can sustain positive changes in their sexual functioning over the long term. CBT provides tools that individuals can continue to use independently even after therapy has ended.
It’s important to note that CBT for sexual dysfunctions is often provided by therapists specialized in sex therapy or with experience in treating sexual dysfunctions. They can tailor the treatment to address the specific needs and concerns of individuals or couples. Additionally, CBT may be used in conjunction with medical interventions, such as medication or medical devices, when appropriate, to provide a comprehensive approach to treating sexual dysfunctions.
Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Right for You?
Determining whether Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is right for you depends on several factors. Here are some considerations to help you determine if CBT is a suitable approach for your needs:
- Focus on Present Concerns: CBT is primarily focused on addressing current problems and difficulties. It places emphasis on identifying and changing thoughts, behaviors, and emotions that contribute to distressing symptoms or patterns. If you are seeking a therapy that directly targets your current concerns and provides practical strategies for managing them, CBT may be a good fit.
- Problem-Solving Orientation: CBT is a goal-oriented and problem-solving therapy. It emphasizes active collaboration between you and your therapist to identify specific goals, develop strategies, and work towards achieving positive changes. If you prefer a structured and action-oriented approach to therapy, CBT may align well with your preferences.
- Willingness to Engage in Homework: CBT often involves homework assignments between therapy sessions. These assignments may include practicing new coping skills, completing thought records, or engaging in behavioral experiments. If you are open to actively participating in the therapeutic process outside of the therapy room and implementing strategies in your daily life, CBT may be a good fit.
- Focus on Thoughts and Behaviors: CBT examines the relationship between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. It emphasizes identifying and challenging unhelpful or negative thought patterns that contribute to distress and adopting healthier beliefs and behaviors. If you are interested in exploring the connection between your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors and making changes in these areas, CBT can be beneficial.
- Preference for Structured and Time-Limited Therapy: CBT typically follows a structured format with a predetermined number of sessions. It aims to provide targeted interventions within a specific timeframe. If you prefer a therapy approach that offers a clear structure and timeline, CBT may be a suitable choice.
- Readiness for Active Participation: CBT requires active participation and engagement from individuals seeking therapy. It involves collaborating with your therapist, setting goals, and actively working on implementing strategies and techniques. If you are ready and motivated to actively participate in therapy, CBT can be an effective approach.
It’s important to note that while CBT has been shown to be effective for many individuals and a range of conditions, it may not be the best fit for everyone. Each person’s therapy needs and preferences are unique, and it can be helpful to consult with a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate approach for your specific situation. They can assess your needs, discuss treatment options, and help you make an informed decision about the therapy that aligns with your goals and preferences.
If you’re struggling with mental health concerns, CBT therapy may be an effective treatment option for you. It’s essential to work with a qualified therapist who can provide you with individualized care tailored to your unique needs and preferences. Take the first step towards achieving lasting relief from your symptoms by exploring the benefits of CBT therapy today.







































