Holistic • Judgement-free • Discreet • Convenient


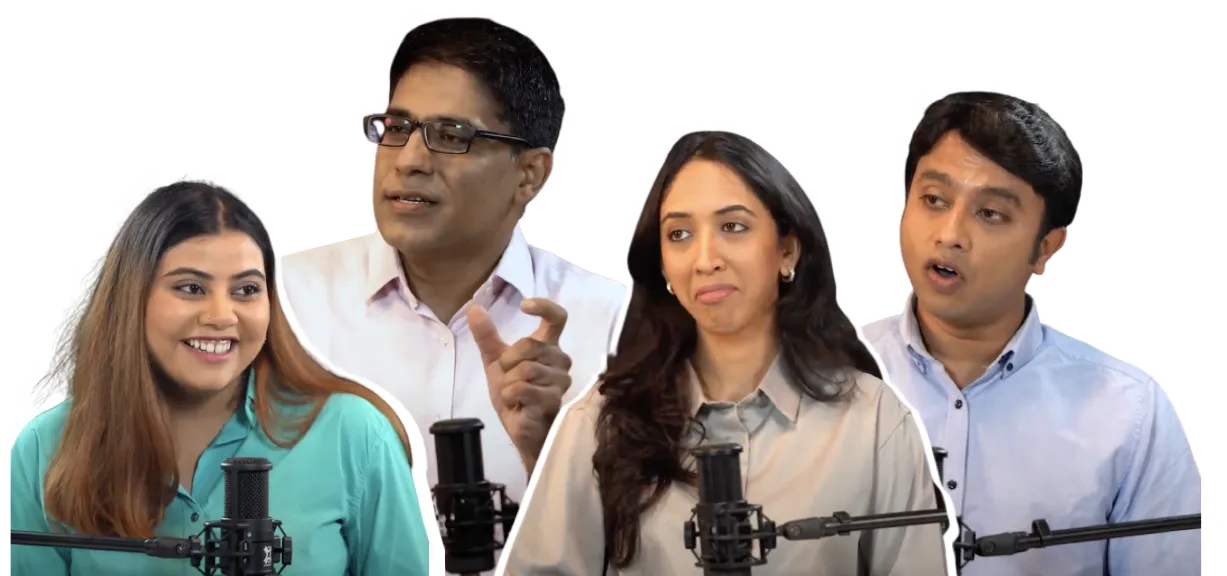
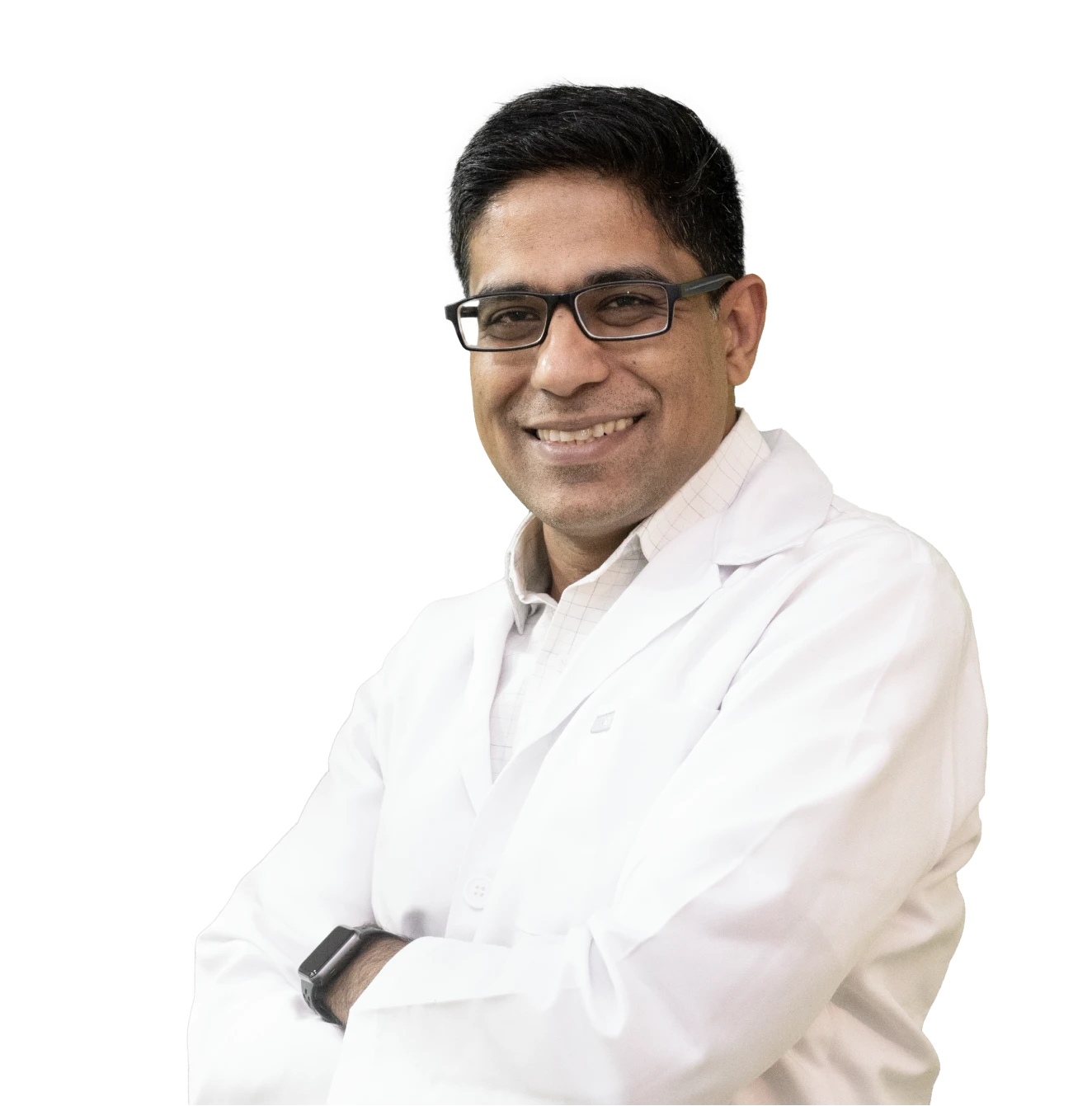
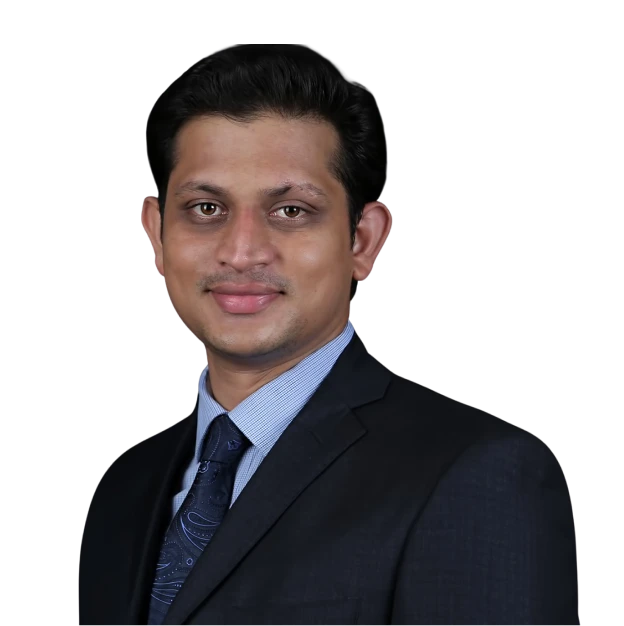
Meet Allo's in-house sexual health experts providing holistic care based on science-backed evidence.


























































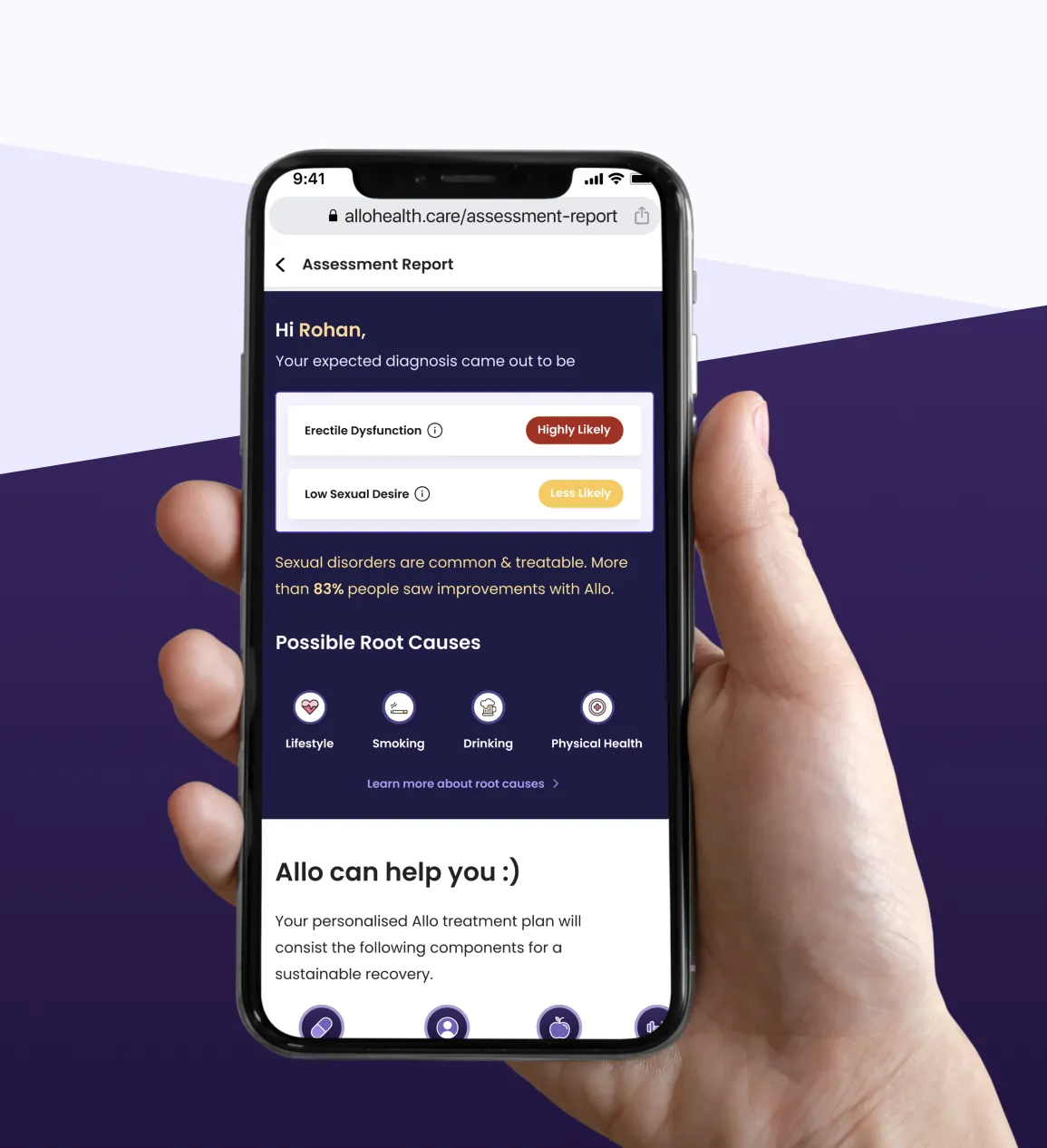



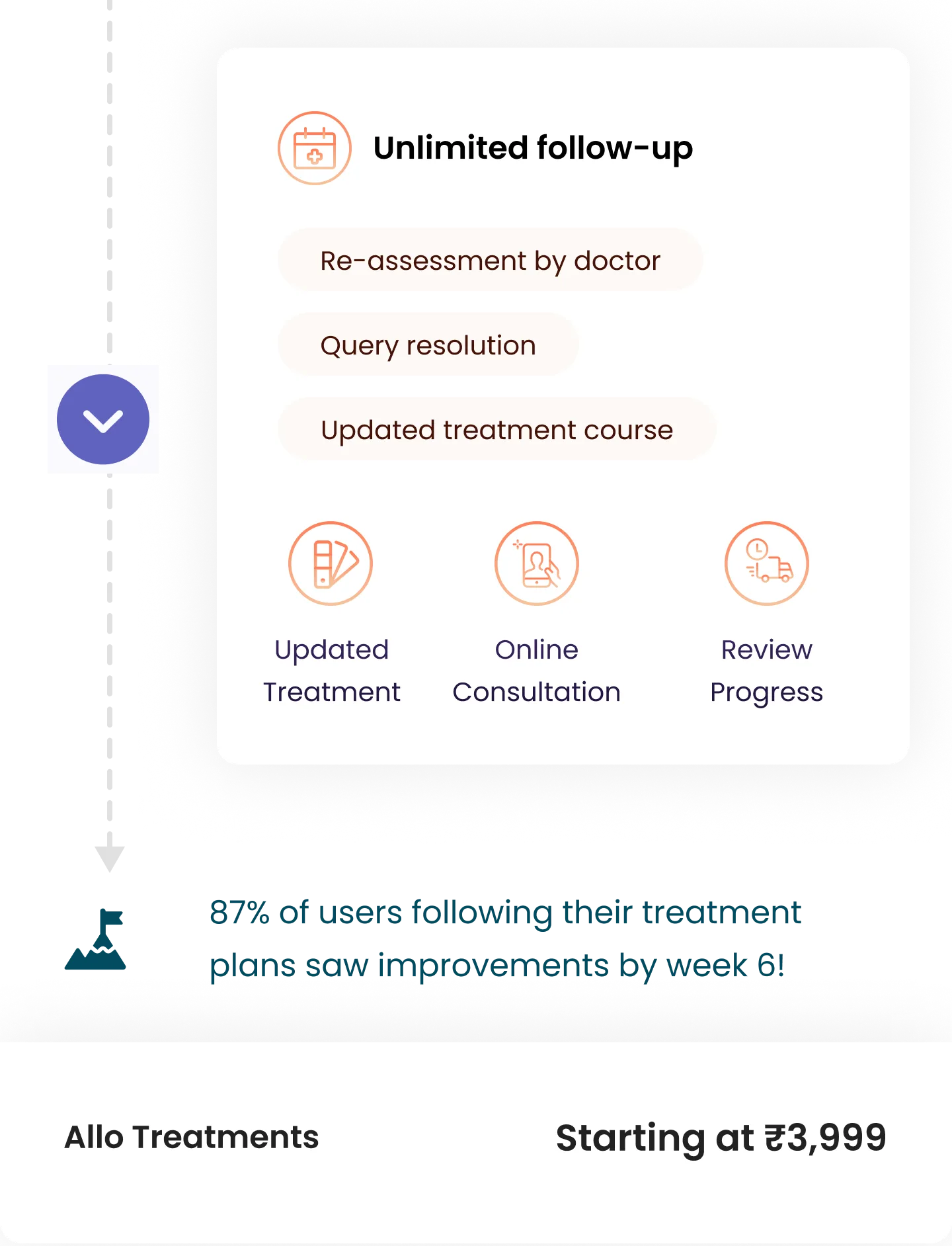
Patients’ treatment journey with Allo

Stories that keeps us going






















Frequently asked questions
You asked we answered

Post your consultation with the doctor, he will recommend the best suited treatment plan for you. Once you decide to purchase the Treatment Plan, our care team will reach out to you and start you on your plan schedule as outlined by your doctor.

Yes, post your purchase, our expert doctor will do a detailed evaluation of your concerns, history & lifestyle to personlise the plan accordingly. The plans shared, show an overview of what to expect in your plan, but each individuals requirements are different & our doctors are specialised in guiding you on your own path towards wellness.

Discreetness and transparency are the cornerstones of Allo’s philosophy. Your data is completely confidential and the details you provide will only be used for honest communication and effective care.

The causes behind erectile dysfunction include psychological conditions, medical/health conditions, certain medications, trauma, hormones, and lifestyle factors.

The causes behind Erectile Dysfunction (ED) include psychological conditions, medical/health conditions, certain medications, trauma, hormones, and lifestyle factors. A physical examination, psychological exam, diagnostic tests such as blood and urine tests, and symptom assessment allows a doctor to diagnose male erectile dysfunction.

The exact cause of premature ejaculation is still not known, but some experts suggest low levels of serotonin can be a causative factor. The psychological causes could be depression/anxiety, relationship problems, and unrealistic expectations.

Various medical treatments can help improve premature ejaculation. Individuals can learn to control their ejaculation for sexual satisfaction through medical remedies, supplements, and exercise. Surgical options such as dividing the nerves to reduce the penile sensations are still considered experimental.

Erectile Dysfunction (ED) refers to the inability to attain or maintain an erection. For Premature Ejaculation (PE), the consensus among specialists is: if a man lasts less than 2 minutes after penetration (all or most of the time), and/or if it leads to frequent dissatisfaction for him or his partner, he may have Premature Ejaculation (PE).

Sexual disorders are much more common than many realize. They can affect relationships emotionally and psychologically. However, addressing sexual dysfunction with a professional can help both partners.

Due to the stigma and rumors associated with "ideal" penis size, many men tend to feel insecure about their manhood. Men commonly worry that the size of their penis is "too small." However, the fact is that a micro penis is one that is less than 3 inches when erect - anything above 3 inches when erect is normal. While it is common for men to feel insecure about this, most women do not care about size. Penile lengthening is considered to be an unsafe and ineffective procedure as per the American Urological Association (AUA).

Sexual performance anxiety is an anxiousness or panic that occurs before, or during sexual intercourse. There are various male performance anxiety solutions - the condition can be treated after a consultation with a professional; some of which include: learning relaxation techniques to help with stress management, managing mental health disorders, seeking couples therapy to aid in interpersonal concerns, and modifying lifestyles such as regular exercise and a healthy diet.

Porn Addiction refers to a person becoming excessively dependent on pornography leading to a disruption in their everyday life. This could include their job, relationships and at times, their day-to-day lifestyle. It is addiction that consists of compulsive sexual activity with the use of any forms of pornographic material, despite the negative consequences. Porn addiction can negatively impact an individual's sex life. For example, it can lead to less satisfying sexual experiences and having high and unreasonable expectations from their partner. Some indicators reveal a porn addiction, such as:- Porn is negatively impacting an individual's life: putting their job or relationship in jeopardy.
- Individuals hide their addiction, and/or feel ashamed or guilty after engaging in porn
- Individuals want to quit the addiction but are emotionally dependent on porn
- Individuals use porn as coping mechanisms One of the side effects a porn addiction is said to have is sexual dysfunction. While it wouldn't be accurate to say that a porn addiction causes sexual dysfunction, it can have a significant impact on an individual’s sexual experiences. Porn is notorious for leading individuals to have fantasy world expectations of sex, and what they or their partner can or can't do. In most cases, individuals find themselves unable to perform to the capacity that they see in porn. It has been revealed that men that have a porn addiction are more likely to experience porn-dependent erectile dysfunction.

Vaginismus is a condition that causes involuntary muscle spasms during sexual intercourse. The psychologically dependent condition disrupts penis-vaginal penetration as the vaginal muscles contract resulting in pain while attempting penile penetration.

Testosterone, the male hormone, is closely associated with a male's sex drive and sexual performance. Low levels of this hormone can cause sexual dysfunction symptoms and disorders such as low libido and erectile dysfunction.

Smoking affects the levels of testosterone in both males and females. This is because it raises carbon monoxide levels in the body which leads to lower production of testosterone which can lead to sexual dysfunctions such as low libido and premature ejaculation. Furthermore, smoking can affect fertility as well making it harder to conceive along with negatively impacting a pregnancy. Men who are smokers commonly have low sperm counts and slow-moving sperm along with concerns about sperm function. Women who are smokers experience egg loss, disruption in ovarian cells responsible for making oestrogen/estrogen, and an increased incidence of genetic abnormalities in their children.

To confirm your consultation with our leading doctors, you will be required to complete payment of ₹199. You can use the screening call to understand your eligibility for Allo Health's Treatment plan and address any other concerns with the doctor.

Post purchase of your care plan, if medicines are prescribed to you, Allo will begin the discreet medication delivery process to the address provided by you. They will be delivered in a standard brown unlabeled package without any mention of the medicine or company name,- just your name and address. You can always find out the status of your medication delivery by contacting your Allo buddy or dedicated care expert through WhatsApp.

Sexual wellness from a holistic point of view caters to both the physical and psychological aspects of any diagnosed condition. There is a major psychological component to sexual disorders, for which we provide uninterrupted access to experts in the field.

Erectile Dysfunction is defined as the inability to sustain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. The condition can affect anyone at any age.

The symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction (ED) include: difficulty in getting an erection, difficulty in maintaining an erection, getting a partial erection, not firm/hard enough for vaginal penetration, reduced libido or sexual desire, increased anxiety and stress associated with sexual intercourse.

Men of any age can experience symptoms of the condition. Besides age, factors such as medical conditions, medications, drinking alcohol, smoking, psychological stress, etc. contribute to Erectile Dysfunction (ED).

If a man lasts less than 2 minutes after penetration (all or most of the time), and/or if it leads to frequent dissatisfaction for him or his partner, he may have Premature Ejaculation (PE).

A method called the stop-start technique works well for Premature Ejaculation (PE). This involves stimulating the penis until just before an orgasm, and then stopping until the urge to ejaculate has gone away. This, when repeated several times, helps a man recognize the phase of arousal that happens before an orgasm.

Sexual dysfunction is a broad term that explains persistent discomfort or difficulty with sexual response, desire, or orgasm. Conditions such as erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation fall under the sexual dysfunction category. Evidence-based and clinically proven sexual dysfunction treatments may include oral tablets, VED (vacuum erection device), injections, and/or surgery - the choice is dependent on the patient’s medical history and treatment plan.

Due to the stigma associated with sexual wellness, people often search for specialists to help them - for example, erectile dysfunction specialists. However, professionals advise you to see an andrologist for anything concerning the internal and external male reproductive system. Some conditions that Andrologists commonly treat organic erectile dysfunction, ejaculatory problems such as premature ejaculation, anejaculation, retrograde ejaculation, and infertility (unable to conceive) due to a male factor.

Retrograde Ejaculation is when semen enters the bladder during orgasm, rather than exiting through the penis. This condition doesn't commonly require treatment unless it disrupts fertility, for which case medications are prescribed to ensure the bladder neck muscles close during ejaculation.

Delayed ejaculation is when an individual requires extended periods of sexual stimulation to ejaculate or reach orgasm. Treatment for this condition is highly dependent on the cause behind it - however, this could include prescribed medications and psychological counseling.

Yes, in the majority of the cases, a physical examination is not required. With technology allowing for the ability to bring about effective solutions, Allo solves for demand in the sexual wellness space. An online consultation reduces unnecessary obstacles such as research, commute, waiting in line, etc without compromising anything for the consumer.

Symptoms of Premature Ejaculations (PE) can be improved through available options such as topical anesthetics and counseling. This is ONLY decided with the help of a professional.

After brief behavioral therapy, the most common first-line medical treatment for Premature Ejaculations (PE) includes tablets from the family of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or phosphodiesterase inhibitors. These medications are prescribed only after a thorough medical examination as some of these medications are contraindicated in certain coexisting medical conditions.

Depending on the cause, erectile dysfunction can be cured. Some causes of Erectile Dysfunction (ED) are easier to cure than others. A medical or psychological evaluation may be necessary to reach the right diagnosis and treatment. Medications may also be prescribed along with psychological intervention.

Impotence is a result of the inability to achieve or maintain an erection or ejaculate consistently. Commonly, impotence is used to describe Erectile Dysfunction (ED), because of the lack of erection sufficient for sexual intercourse.

While it is common knowledge that physical medical conditions or injuries can lead to sexual dysfunction, the fact that mental health conditions can also be a cause is often missed. When experiencing conditions such as depression and anxiety, an individual's mind and body are in a constant state of stress. This leads to the release of a hormone called cortisol - chronic high levels of this hormone can lead to the decrease of testosterone in the body. Low testosterone can lead to conditions such as low libido and erectile dysfunction. Depression is also characterised by a general lack of drive in all activities including sexual intimacy.

An unconsummated marriage (UM) or a relationship is defined by a heterosexual couple’s inability to have penetrative vaginal intercourse. Many couples experience an unconsummated relationship, and while there is an unnecessary stigma associated with it, it can be treated or improved with the help of a professional. It could be a result of contributing factors from him or her or both.

Aerobic and pelvic floor exercises are highly recommended as a lifestyle modification while dealing with sexual dysfunction or disorders. These types of exercises help improve incontinence, manage conditions such as prostatitis and BPH, and of course, increase male sexual pleasure by helping men have greater control over ejaculation and orgasm. Cardio exercises help in keeping the blood vessels clear, and so, have the ability to improve one’s sex life. Sexual dysfunctions such as ED, are commonly caused by problems with the blood flow to the penis. Factors such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or concerns in weight management leading to obesity, can affect blood flow and lead to ED symptoms. Aerobic exercises help in all these conditions and improve sexual functioning.

From medications to psychosexual therapy, there are ways to help treat the symptoms of ED, PE, and other sexual disorders. However, many often forget that their lifestyle habits can bring about changes in their sexual health as well. One lifestyle modification that many take for granted is diet — a bad diet can cause many things from medical conditions such as hypertension to affecting sexual health and function. For example, there are foods that improve erectile function by aiding in improved blood flow, and increased testosterone and nitric oxide production.

Alcohol has the ability to interfere with sexual stimulation by disrupting the signals sent between the brain and the genitals. It is common for those with alcoholism to experience low sexual desire, disruption in arousal (lubrication in women, and erection in men), and ejaculation disorders (such as delayed ejaculation).

Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that leads to lower levels of testosterone which can lead to sexual dysfunction symptoms. Furthermore, it can also alter brain signals needed for the genital organs to have optimal blood flow during sexual activity.

Female sexual arousal disorder (FSAD) is a condition in which the individual's body does not respond to sexual stimulation. It is a sexual dysfunction that is very common but treatable. Some symptoms of FSAD include low sexual desire or libido, lack of sexual thoughts, decreased sexual excitement, reduced arousal from internal or external stimulation, and lack of sensation in the genitalia or other arousal parts of the body.

Anorgasmia is a condition in which individuals are unable to orgasm despite medical intervention or sexual stimulation. It is much more prevalent in females/women and is commonly caused by psychological factors. However, there are medical conditions or medications/treatments for medical conditions that can cause anorgasmia.

Women experience hormone fluctuations as they age and when estrogen levels drop very low (commonly during the 40s and 50s), they go through menopause. The low levels of estrogen can lead to a negative impact on sexual wellness - for example, it can lead to low libido, vaginal dryness, or lack of lubrication leading to painful sex and disrupted mood and sleep patterns.

Post your consultation with the doctor, he will recommend the best suited treatment plan for you. Once you decide to purchase the Treatment Plan, our care team will reach out to you and start you on your plan schedule as outlined by your doctor.

Yes, post your purchase, our expert doctor will do a detailed evaluation of your concerns, history & lifestyle to personlise the plan accordingly. The plans shared, show an overview of what to expect in your plan, but each individuals requirements are different & our doctors are specialised in guiding you on your own path towards wellness.

Discreetness and transparency are the cornerstones of Allo’s philosophy. Your data is completely confidential and the details you provide will only be used for honest communication and effective care.

The causes behind erectile dysfunction include psychological conditions, medical/health conditions, certain medications, trauma, hormones, and lifestyle factors.

The causes behind Erectile Dysfunction (ED) include psychological conditions, medical/health conditions, certain medications, trauma, hormones, and lifestyle factors. A physical examination, psychological exam, diagnostic tests such as blood and urine tests, and symptom assessment allows a doctor to diagnose male erectile dysfunction.

The exact cause of premature ejaculation is still not known, but some experts suggest low levels of serotonin can be a causative factor. The psychological causes could be depression/anxiety, relationship problems, and unrealistic expectations.

Various medical treatments can help improve premature ejaculation. Individuals can learn to control their ejaculation for sexual satisfaction through medical remedies, supplements, and exercise. Surgical options such as dividing the nerves to reduce the penile sensations are still considered experimental.