Amoxicillin 500mg Dosage for Syphilis: What You Need to Know

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr. Aditi completed her undergraduate medical education at AJIMS, Mangalore, after which she worked in multi-speciality hospitals with COVID patients and in the Pain and Palliative medicine department. Driven by her experiences, she developed a keen interest in psychiatry. Dr. Aditi believes that mental health is just as, if not more important, than physical health.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 10 February, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.

"The following blog article provides information about a drug or brand name drug and its potential effects or benefits. However, it is crucial to understand that this information is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical consultation. It is highly recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions regarding medication, treatment, or healthcare management.
Book consultation
Individuals have unique medical conditions, and the information provided in this article may not be applicable to everyone. Only a qualified healthcare provider can evaluate your specific medical situation, taking into account your medical history, conducting appropriate tests, and providing personalized advice and recommendations. They are equipped to make informed decisions tailored to your individual needs.
It is crucial to emphasize that self-diagnosis, self-medication, or disregarding medical advice can have serious health consequences. This article may reference specific brand names or drugs for illustrative purposes. Mention of these names does not imply endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of their efficacy or safety. The choice of medication should be based on discussions and individualized guidance from a healthcare professional who has a comprehensive understanding of your medical condition.
"Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. If left untreated, syphilis can lead to serious health concerns, such as blindness, neurological damage, and even death. Fortunately, syphilis can be effectively treated with antibiotics like amoxicillin.
Syphilis Overview
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It has four stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. If left untreated, syphilis can lead to severe complications, including damage to the heart, brain, and other organs.
Here’s an overview of each stage:
- Primary Syphilis:
- The first sign is usually a painless sore or ulcer called a chancre.
- The chancre appears at the site of infection, typically genitals, anus, or mouth, and it lasts 3-6 weeks.
- Because the sore is painless, it may go unnoticed.
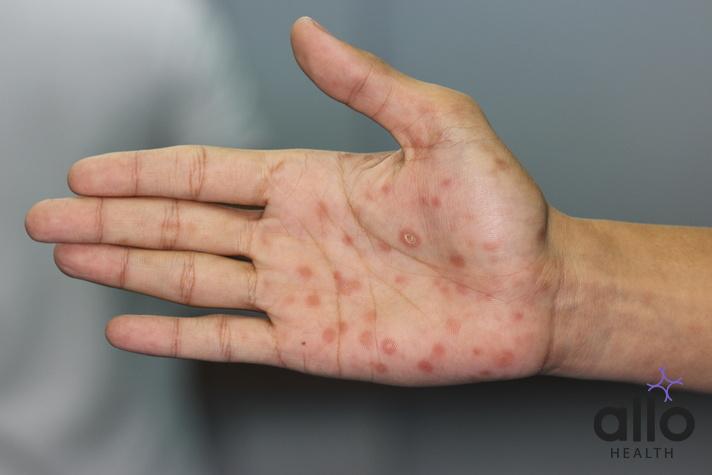
- Secondary Syphilis:
- Symptoms may appear 2 to 10 weeks after the appearance of the chancre.
- Common symptoms include skin rash (usually on the palms and soles), mucous membrane lesions, fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, and muscle aches.
- The rash can vary in appearance and may be rough, red, or reddish-brown spots.
- Latent Syphilis:
- If not treated, syphilis progresses to the latent stage.
- During this stage, there are no visible symptoms, but the bacteria can still be present in the body.
- Latent syphilis is further divided into early latent (within the first year) and late latent (after one year).
- Tertiary Syphilis:
- Tertiary syphilis can occur years after the initial infection.
- This stage can lead to severe complications affecting various organs, such as the heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and nervous system.
- Neurosyphilis, a form of tertiary syphilis, can cause a range of neurological symptoms, including difficulty coordinating muscle movements, paralysis, and mental health concerns.
Syphilis is typically diagnosed through blood tests. The most common treatment is penicillin, an antibiotic effective against the bacterium. In some cases, other antibiotics may be used for individuals allergic to penicillin.
Prevention includes practicing safe sex by using condoms, knowing your partner’s sexual health history, and getting regular STI screenings. Pregnant women with syphilis can transmit the infection to their babies, so it’s crucial for pregnant individuals to undergo routine prenatal care and be screened for syphilis.
Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent complications and the spread of the infection. If you suspect you have syphilis or have been exposed to it, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for testing and appropriate care.

Amoxicillin Overview
Amoxicillin is a widely used antibiotic belonging to the penicillin group. It is effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria and is commonly prescribed for various bacterial infections. Here’s a detailed overview:
Mechanism of Action:
- Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. It does so by interfering with the cross-linking of peptidoglycans, essential components of bacterial cell walls. This weakens the cell wall, leading to bacterial cell death.
Spectrum of Activity:
- Amoxicillin has a broad spectrum of activity, making it effective against a wide range of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms.
- It is commonly used to treat respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, ear infections, and some sexually transmitted infections.
Formulations:
- Amoxicillin is available in various formulations, including oral tablets, capsules, chewable tablets, and pediatric suspensions.
- Extended-release formulations are also available, allowing for less frequent dosing.
Dosage:
- Dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient’s age and weight.
- It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and complete the entire course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
Adverse Effects:
- Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and rash.
- Allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, and more severe reactions like anaphylaxis, can occur in some individuals, especially those with a history of penicillin allergy.
- Long-term use or misuse of antibiotics can lead to the development of antibiotic resistance.
Precautions and Contraindications:
- Amoxicillin should be used with caution in individuals with a history of allergic reactions to penicillins or cephalosporins.
- Patients with infectious mononucleosis (mono) may be at an increased risk of developing a skin rash if treated with amoxicillin.
- It is important to inform healthcare providers about any pre-existing medical conditions or medications being taken to avoid potential interactions.
Pregnancy and Lactation:
- Amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy and lactation when prescribed by a healthcare professional. However, the risks and benefits should be carefully evaluated.
Interactions:
- Amoxicillin may interact with certain medications, including oral contraceptives and medications that reduce stomach acid.
Storage:
- Amoxicillin should be stored according to the specific instructions on the medication packaging.
- It is essential to check the expiration date and discard any unused medication after the prescribed period.
Amoxicillin is a valuable and commonly prescribed antibiotic, but it should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It is crucial to complete the prescribed course to ensure the effective treatment of bacterial infections and to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance. If someone experiences adverse effects or has concerns about the medication, they should consult their healthcare provider.
Amoxicillin 500mg Dosage for Syphilis: What You Need to Know
Syphilis is typically treated with penicillin, which is the preferred antibiotic for this infection. However, amoxicillin, a related antibiotic, may be used as an alternative in certain situations, such as when penicillin is not tolerated.
If amoxicillin is prescribed for syphilis, the dosage can vary based on factors such as the stage of the infection, the patient’s weight, and individual considerations. It’s crucial to follow the specific instructions provided by the prescribing healthcare professional.
As an example, a common dosage for adults in the treatment of syphilis might be:
- Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times a day for 10 to 14 days.
This is just a general example, and the actual dosage can vary. The duration of treatment and the specific dosage should be determined by a healthcare professional based on factors such as the stage of syphilis, the patient’s overall health, and any potential allergies or sensitivities.
It’s important to note that the treatment of syphilis requires careful medical supervision. It is not recommended to self-diagnose or self-treat syphilis without consulting a healthcare professional. Untreated or inadequately treated syphilis can lead to serious complications.
If you suspect you have syphilis or have been diagnosed with syphilis, it’s crucial to seek prompt medical attention. Your healthcare provider will conduct appropriate tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific situation. Always take antibiotics exactly as prescribed, and complete the entire course of treatment to ensure the infection is effectively cleared.
Most Asked Questions
-
Is amoxicillin 500mg an appropriate dosage for syphilis remedy?
Yes, amoxicillin 500mg may be a suitable dosage for treating syphilis, but the precise dosage and length can also vary based on man or woman elements along with the level of syphilis and affected person traits. Always observe the healthcare professional's prescribed dosage.
-
Can I self-prescribe amoxicillin 500mg for syphilis?
No, self-prescribing antibiotics, which include amoxicillin, is strongly discouraged. Syphilis remedy calls for a unique diagnosis and the suitable antibiotic routine determined by means of a healthcare professional. Self-remedy can result in insufficient remedy, allowing the infection to persist and potentially expand resistance to antibiotics.
-
How long should I take amoxicillin 500mg for syphilis?
The length of amoxicillin remedy for syphilis varies based totally on the stage of the infection and the healthcare provider's suggestions. It is crucial to finish the total direction of antibiotics as prescribed, even though signs improve before of entirety, to ensure the contamination is fully eradicated.
-
Are there any side outcomes related to amoxicillin 500mg for syphilis?
Common side effects of amoxicillin may include nausea, diarrhea, and rash. It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider of any adverse reactions. Severe allergic reactions can occur, and if you experience symptoms like swelling or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
-
Can pregnant people take amoxicillin 500mg for syphilis at some stage in pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals should consult their healthcare provider for guidance on syphilis treatment. While amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy, healthcare professionals will carefully assess the risks and benefits to ensure the well-being of both the pregnant person and the developing fetus. Never self-prescribe antibiotics during pregnancy without professional advice.






































